HEA and HEB steel beams are European standard wide flange beams used extensively in construction and engineering. HEA beams, characterized by their lighter weight and thinner flanges, are ideal for applications requiring efficiency without heavy load-bearing needs. HEB beams, with their thicker flanges and greater depth, provide enhanced strength and rigidity, making them suitable for a wide range of structural applications where higher load capacity is necessary. Both types offer versatility and reliability for modern architectural and structural designs.
HEA/HEB STEEL BEAMS
WHAT ARE HEA STEEL BEAMS
HEA steel beams are a type of European standard wide flange beam, characterized by their “H” cross-section where the dimensions of the flanges and the web are in approximate proportion. The acronym “HEA” stands for “High Edge (or European) A,” indicating that these beams have relatively wider flanges and thinner webs compared to other types of structural steel beams.

HEA Beams Features:
- Lightweight Design: HEA beams are designed to be lighter than HEB and HEM beams, making them a preferred choice for structures where weight saving is crucial without significantly compromising structural integrity.
- Flange and Web Proportions: The flanges of HEA beams are wider and thinner, offering a good balance between strength and flexibility, which is advantageous for architectural and structural applications that require both.
- Applications: HEA beams are commonly used in the construction of commercial and residential buildings, frames for roofs and floors, bridges, and other structures where efficient support is needed without excessive bulk.
- Manufacturing Standards: They are manufactured following European standards, which ensure consistent quality and performance across all HEA beams.
WHAT ARE HEB STEEL BEAMS
HEB steel beams are a type of wide flange beam commonly used in construction and engineering projects across Europe and globally. The acronym “HEB” stands for “High Edge (or European) B,” indicating a series of beams with a broad flange and greater depth compared to HEA beams, making them stronger and more suitable for carrying heavier loads.

HEB Steel Beams Features
- Robust Design: HEB beams feature a stronger and heavier design than HEA beams. Their flanges and webs are thicker, which contributes to their higher load-bearing capacity.
- Proportions: They have a wide flange and a thick web, providing excellent resistance against bending and shear forces. The proportion of their dimensions is designed to optimize structural efficiency in various applications.
- Applications: Due to their robustness, HEB beams are widely utilized in the construction of industrial buildings, bridges, heavy infrastructure, and where large spans or heavy loads are involved. They are also preferred in environments that require high structural integrity and durability.
- Manufacturing Standards: Like HEA beams, HEB beams are manufactured according to European standards, ensuring high quality, reliability, and uniformity across all beams.
DIFFERENCE HEA VS. HEB BEAM
While HEA and HEB structural steel beams share some similarities, including their H-shaped cross-section, there are key differences in their dimensions and applications that make each suited to specific structural needs.
HEA (High Edge A) Steel Beams
- Design: Characterized by their relatively wider flanges and thinner web, HEA beams offer a good balance between strength and flexibility. The “A” signifies that these beams are lighter, with a lower profile compared to HEB beams.
- Weight and Dimensions: HEA beams are designed to be lighter, which makes them a practical choice for structures where saving on weight is beneficial without heavily compromising on structural integrity.
- Applications: Ideal for applications where the load is relatively moderate, such as in residential or commercial building frameworks, non-load-bearing walls, and architectural projects.
HEB (High Edge B) Steel Beams
- Design: HEB beams have thicker webs and wider flanges than HEA beams, which makes them stronger and more rigid. The “B” indicates a heavier beam profile with a higher load-bearing capacity.
- Weight and Dimensions: Due to their design, HEB beams are heavier and provide greater structural support, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Applications: HEB beams are typically used in projects requiring enhanced structural support, including large commercial buildings, bridges, and supports for heavy machinery or loads.
Key Differences
- Structural Strength and Load Capacity: HEB beams are stronger and have a higher load capacity due to their thicker flanges and webs, making them suitable for more demanding structural applications.
- Weight: HEA beams are lighter, which may reduce material costs and facilitate easier handling and construction, especially in projects where the maximum strength of HEB beams isn’t necessary.
- Dimensional Variety: Both HEA and HEB beams come in a range of sizes, but the specific dimensions and weight of each beam type cater to different structural needs and preferences.
Difference between HEA/HEB vs. HEM beams
Consult the linked article to learn about the key differences between HEM, HEA, and HEB beams.
EN SPECIFICATIONS FOR HEA/HEB BEAMS
The European standards (EN) provide specifications for the dimensions, tolerances, and physical properties of structural steel sections, including HEA (High Edge A) and HEB (High Edge B) steel beams. These specifications ensure consistency and quality across products used in construction and engineering projects within Europe and globally. The primary EN standards relevant to HEA and HEB steel beams are:
EN 10034: Structural Steel I and H Sections; Tolerances on Shape and Dimensions
This standard specifies the tolerance requirements for the shape and dimensions of structural steel I and H sections, which include HEA and HEB beams. It covers aspects such as straightness, depth, width, web and flange thickness, and mass per unit length.
EN 10025: Hot Rolled Products of Structural Steels
EN 10025 is a series of standards that outline the requirements for the chemical composition and mechanical properties of hot-rolled structural steel products. Although it encompasses various types of structural steels, including those used to manufacture HEA and HEB beams, it ensures the steel used meets certain criteria for strength and durability.
The EN 10025 specification for European steel beams is divided into multiple parts (e.g., EN 10025-2 for non-alloy structural steels), each focusing on a specific category of steel with its own set of properties and applications.
EN 10365: Hot Rolled Steel Channels, I and H Sections; Dimensions and Masses
EN 10365 provides detailed specifications for the dimensions and masses of hot-rolled steel channels, I-sections (which include HEA and HEB beams), and H-sections. It includes comprehensive tables that list the dimensions and mass (weight per meter) for each beam size, facilitating precise design and engineering calculations.
COMMON MATERIAL GRADES
The common steel grades used for HEA and HEB beams in construction and engineering projects are typically carbon and low-alloy steels, which are outlined in several EN standards. These material grades are selected based on their mechanical properties, weldability, toughness, and suitability for various environmental conditions.
EN 10025 S235JR
- Standard: EN 10025-2
- Characteristics: S235JR is a non-alloy structural steel grade with good weldability. This grade offers a blend of strength and ductility, which is suitable for general construction purposes.
EN 10025 S275JR
- Standard: EN 10025-2
- Characteristics: Slightly higher in strength than S235JR, S275JR steel is also a non-alloy structural grade with excellent weldability. It is used in structural and construction applications where higher strength is required.
EN 10025 S355J2
- Standard: EN 10025-2
- Characteristics: S355J2 is a high-strength, low-alloy structural steel grade with superior mechanical properties and enhanced resistance to atmospheric corrosion. It is well-suited for load-bearing structures and for use in harsh environmental conditions.
EN 10025 S355K2
- Standard: EN 10025-2
- Characteristics: Similar to S355J2, S355K2 is another high-strength, low-alloy structural steel. However, it has improved impact strength, especially at lower temperatures, making it ideal for structural applications in cold climates.
Selection Considerations
- Mechanical Properties: The choice of material grade is influenced by the required mechanical properties, such as yield strength and tensile strength, which determine the beam’s load-bearing capacity.
- Environmental Conditions: Steel grades with enhanced resistance to corrosion, like certain variations of S355 steel, are preferred for outdoor applications or in environments prone to corrosive elements.
- Weldability and Fabrication: Grades with good weldability are essential for construction projects to ensure strong and durable welded joints.
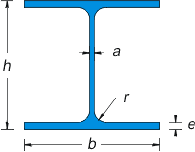
DIMENSION & WEIGHTS HEA/BEH STEEL BEAMS
H Steel beams HEA/HEB are a very commonly used type of steel profile. Beams, otherwise called “H” sections, continental beams, or HEA/HEB, are available in multiple material grades, the most common are EN 10025 S275, and S355. H sections look similar to I sections, but the flange is wider.
HEA Beams Sizes, and Mechanical Properties
| HEA Beams Sizes | Weight (kg/m) | Sectional Area (cm2) | Inertial Moment | Resistance Modules | Inertial Radius | |||||||
| b | h | a | e | r | Jx (cm4) | Jy (cm4) | Wx (cm3) | Wy (cm3) | ix (cm) | iy (cm) | ||
| HEA 100 | 96 | 5,0 | 8,0 | 12 | 16,7 | 21,24 | 349,2 | 133,8 | 72,76 | 26,76 | 4,06 | 2,51 |
| HEA 120 | 114 | 5,0 | 8,0 | 12 | 19,9 | 25,34 | 606,2 | 230,9 | 106,3 | 38,48 | 4,89 | 3,02 |
| HEA 140 | 133 | 5,5 | 8,5 | 12 | 24,7 | 31,42 | 1.033 | 389,3 | 155,4 | 55,62 | 5,73 | 3,52 |
| HEA 160 | 152 | 6,0 | 9,0 | 15 | 30,4 | 38,77 | 1.673 | 615,6 | 220,1 | 76,95 | 6,57 | 3,98 |
| HEA 180 | 171 | 6,0 | 9,5 | 15 | 35,5 | 45,25 | 2.51 | 924,6 | 293,6 | 102,7 | 7,45 | 4,52 |
| HEA 200 | 190 | 6,5 | 10,0 | 18 | 42,3 | 53,83 | 3.692 | 1.326 | 388,6 | 133.6 | 8,28 | 4,98 |
| HEA 220 | 210 | 7,0 | 11,0 | 18 | 50,5 | 64,34 | 5.41 | 1.955 | 515,2 | 177,7 | 9,17 | 5,51 |
| HEA 240 | 230 | 7,5 | 12,0 | 21 | 60,3 | 76,84 | 7.763 | 2.769 | 675,1 | 230,7 | 10,05 | 6,00 |
| HEA 260 | 250 | 7,5 | 12,5 | 24 | 68,2 | 86,82 | 10.45 | 3.668 | 836,4 | 282,1 | 10,97 | 6,50 |
| HEA 280 | 270 | 8,0 | 13,0 | 24 | 76,4 | 97,26 | 13.67 | 4.763 | 1.013 | 340,2 | 11,86 | 7,00 |
| HEA 300 | 290 | 8,5 | 14,0 | 27 | 88,3 | 112,5 | 18.26 | 6.31 | 1.26 | 420,6 | 12,74 | 7,49 |
| HEA 300 | 310 | 9,0 | 15,5 | 27 | 97,6 | 124,4 | 22.93 | 6.985 | 1.479 | 465,7 | 13,58 | 7,49 |
| HEA 300 | 330 | 9,5 | 16,5 | 27 | 105,0 | 133,5 | 27.69 | 7.436 | 1.678 | 495,7 | 14,40 | 7,46 |
| HEA 300 | 350 | 10,0 | 17,5 | 27 | 112,0 | 142,8 | 33.09 | 7.887 | 1.891 | 525,8 | 15,22 | 7,43 |
| HEA 300 | 390 | 11,0 | 19,0 | 27 | 125,0 | 159,0 | 45.07 | 8.564 | 2.311 | 570.9 | 16,84 | 7,34 |
| HEA 300 | 440 | 11,5 | 21,0 | 27 | 140,0 | 178,0 | 63.72 | 9.465 | 2.896 | 631,0 | 18,92 | 7,29 |
| HEA 300 | 490 | 12,0 | 23,0 | 27 | 155,0 | 197,5 | 86.97 | 10.37 | 3.55 | 691,1 | 21,98 | 7,24 |
| HEA 300 | 540 | 12,5 | 24,0 | 27 | 166,0 | 211,8 | 111.9 | 10.82 | 4.146 | 721,3 | 22,99 | 7,15 |
| HEA 300 | 590 | 13,0 | 25,0 | 27 | 178,0 | 226,5 | 141.2 | 11.27 | 4.787 | 751,4 | 24,97 | 7,05 |
| HEA 300 | 640 | 13,5 | 26,0 | 27 | 190,0 | 241,6 | 175.2 | 11.72 | 5.474 | 781,6 | 26,93 | 6,97 |
| HEA 300 | 690 | 14,5 | 27,0 | 27 | 204,0 | 260,5 | 215.3 | 12.18 | 6.241 | 811,9 | 28,87 | 6,84 |
| HEA 300 | 790 | 15,0 | 28,0 | 30 | 224,0 | 285,8 | 303.4 | 12.64 | 7.682 | 842,6 | 32,58 | 6,65 |
| HEA 300 | 890 | 16,0 | 30,0 | 30 | 252,0 | 320,5 | 422.1 | 13.55 | 9.485 | 903,2 | 36,29 | 6,50 |
| HEA 300 | 990 | 16,5 | 31,0 | 30 | 272,0 | 346,8 | 553.8 | 14 | 11.19 | 933,6 | 39,96 | 6,35 |
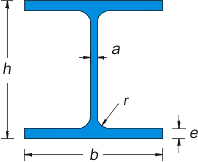
HEB Beams Sizes, and Mechanical Properties
| HEB Beam Sizes | Weight (kg/m) | Sectional Area (cm2) | Inertial Moment | Resistance Modules | Inertial Radius | |||||||
| b | h | a | e | r | Jx (cm4) | Jy (cm4) | Wx (cm3) | Wy (cm3) | ix (cm) | iy (cm) | ||
| HEB 100 | 100 | 6,0 | 10,0 | 12 | 20,4 | 26,04 | 449,5 | 167,3 | 89,91 | 33,45 | 4,16 | 2,53 |
| HEB 120 | 120 | 6,5 | 11,0 | 12 | 26,7 | 34,01 | 864,4 | 317,5 | 144,1 | 52,92 | 5,04 | 3,06 |
| HEB 140 | 140 | 7,0 | 12,0 | 12 | 33,7 | 42,96 | 1.509 | 549,7 | 215,6 | 78,52 | 5,93 | 3,58 |
| HEB 160 | 160 | 8,0 | 13,0 | 15 | 42,6 | 54,25 | 2.492 | 889,2 | 311,5 | 111,2 | 6,78 | 4,05 |
| HEB 180 | 180 | 8,5 | 14,0 | 15 | 51,2 | 65,25 | 3.831 | 1.363 | 425,7 | 151,4 | 7,66 | 4,57 |
| HEB 200 | 200 | 9,0 | 15,0 | 18 | 61,3 | 78,08 | 5.696 | 2.003 | 569,6 | 200,3 | 8,54 | 5,07 |
| HEB 220 | 220 | 9,5 | 16,0 | 18 | 71,5 | 91,04 | 8.091 | 2.843 | 735,5 | 258,5 | 9,43 | 5,59 |
| HEB 240 | 240 | 10,0 | 17,0 | 21 | 83,2 | 106,0 | 11.26 | 3.923 | 938,3 | 326,9 | 10,31 | 6,08 |
| HEB 260 | 260 | 10,0 | 17,5 | 24 | 93,0 | 118,4 | 14.92 | 5.135 | 1.148 | 395,0 | 11,22 | 6,58 |
| HEB 280 | 280 | 10,5 | 18,0 | 24 | 103,0 | 131,4 | 19.27 | 6.595 | 1.376 | 471,0 | 12,11 | 7,09 |
| HEB 300 | 300 | 11,0 | 19,0 | 27 | 117,0 | 149,1 | 25.17 | 8.563 | 1.678 | 570,9 | 12,99 | 7,58 |
| HEB 300 | 320 | 11,5 | 20,5 | 27 | 127,0 | 161,3 | 30.82 | 9.239 | 1.926 | 615,9 | 13,82 | 7,57 |
| HEB 300 | 340 | 12,0 | 21,5 | 27 | 134,0 | 170,9 | 36.66 | 9.69 | 2.156 | 646,0 | 14,65 | 7,53 |
| HEB 300 | 360 | 12,5 | 22,5 | 27 | 142,0 | 180,6 | 43.19 | 10.14 | 2.4 | 676,1 | 15,46 | 7,49 |
| HEB 300 | 400 | 13,5 | 24,0 | 27 | 155,0 | 197,8 | 57.68 | 10.82 | 2.884 | 721,3 | 17,08 | 7,40 |
| HEB 300 | 450 | 14,0 | 26,0 | 27 | 171,0 | 218,0 | 79.89 | 11.72 | 3.551 | 781,4 | 19,14 | 7,33 |
| HEB 300 | 500 | 14,5 | 28,0 | 27 | 187,0 | 238,6 | 107.2 | 12.62 | 4.287 | 841,6 | 21,19 | 7,27 |
| HEB 300 | 550 | 15,0 | 29,0 | 27 | 199,0 | 254,1 | 136.7 | 13.08 | 4.971 | 871,8 | 23,20 | 7,17 |
| HEB 300 | 600 | 15,5 | 30,0 | 27 | 212,0 | 270,0 | 171 | 13.53 | 5.701 | 902,0 | 25,17 | 7,08 |
| HEB 300 | 650 | 16,0 | 31,0 | 27 | 225,0 | 286,3 | 210.6 | 13.98 | 6.48 | 932,3 | 27,12 | 6,99 |
| HEB 300 | 700 | 17,0 | 32,0 | 27 | 241,0 | 306,4 | 256.9 | 14.44 | 7.34 | 962,7 | 28,96 | 6,87 |
| HEB 300 | 800 | 17,5 | 33,0 | 30 | 262,0 | 334,2 | 359.1 | 14.9 | 8.977 | 993,6 | 32,78 | 6,68 |
| HEB 300 | 900 | 18,5 | 35,0 | 30 | 291,0 | 371,3 | 494.1 | 15.82 | 10.98 | 1.054 | 36,48 | 6,53 |
| HEB 300 | ### | 19,0 | 36,0 | 30 | 314,0 | 400,0 | 644.7 | 16.28 | 12.89 | 1.085 | 40,15 | 6,38 |


4 Responses
i have a h beam for sale. roughly 40 ft long. 6inches wide, 9-1/2inches wide and 5/8thick
How much are u going to sell and where is your location. Reply if it’s still available
200 X 200 X 9 X 15 HEB BEAM LENGTH:12 METER GRADE : A 61.3KG/MTR QTY 26 NOS
I would like to know a length of 4.5metres HEB 140 and 240 may carry?