Forged Fittings: SW & Threaded (B16.11)
Forged Fittings ASME B16.11
What Are Forged Fittings?
ASME B16.11 covers socket-welding and threaded forged fittings, the workhorses of small-bore piping. If you have been around any plant long enough, you have seen thousands of these: every instrument connection, every drain, every vent, every small process tie-in.

The forging process shapes solid steel billets under high pressure, which produces a tighter grain structure than casting. In practice, this means forged fittings handle pressure, thermal cycling, and vibration far better than cast equivalents. They are the default choice for high-pressure, high-temperature, and corrosive service.

Socket/Threaded Fittings in ASME B16.11
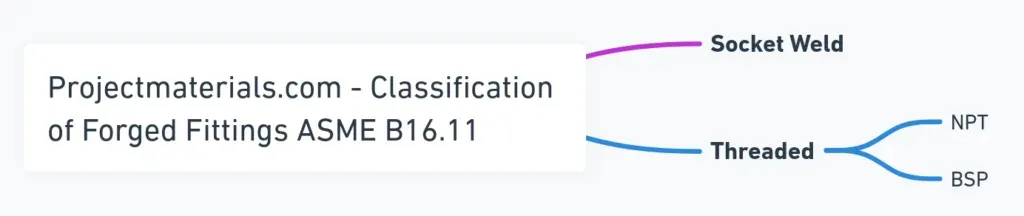 FOrged fittings by end connection
FOrged fittings by end connection
The two connection types in B16.11 differ fundamentally in how they join to pipe:
| Connection | Method | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Socket Weld (SW) | Pipe inserts into fitting socket; fillet weld applied around the joint | High-pressure, critical service (steam, hydrocarbons, toxic fluids) |
| Threaded (THD) | Pipe screws into fitting via NPT or BSP threads | Lower-pressure, non-critical service (utilities, drains, instrument taps) |
Sizes and Pressure Ratings
B16.11 covers NPS 1/8” through 4”. Class ratings match specific pipe schedules; get this wrong and you create a weak point at the joint (see the caution note below).
What Does “Class” Mean for Forged Fittings?
The class number roughly corresponds to the maximum cold working pressure in psi. More importantly, it tells you which pipe schedule the fitting pairs with:
| Class | Max Pressure (approx.) | Matching Pipe Schedule |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | Up to 2,000 psi | Sch 40 (threaded only) |
| 3000 | Up to 3,000 psi | Sch 80 |
| 6000 | Up to 6,000 psi | Sch 160 |
| 9000 | Up to 9,000 psi | XXS |
Actual allowable pressure drops with temperature. B16.11 has detailed P/T tables by material grade. Always check these tables rather than assuming room-temperature values apply at operating conditions. Select class based on maximum operating pressure, design temperature, and material compatibility with the process fluid.
Forged vs. Buttweld Fittings
| Aspect | Forged (B16.11) | Buttweld (B16.9) |
|---|---|---|
| Size range | NPS 1/8”-4” (2000#/3000#) or 1/8”-2” (6000#/9000#) | NPS 1/2” and up |
| Raw material | Solid steel billets, machined to shape | Seamless or welded pipe, cut and formed |
| Connection | Socket weld (fillet weld) or threaded | Butt weld (full-penetration weld) |
| Specs | ASME B16.11, MSS SP-75, SP-83, SP-95 | ASME B16.9 |
Forged fittings pair with ASME B36.10 and B36.19 small-bore pipes in carbon, alloy, stainless, and nickel alloy grades.
Applicable Specifications (ASME/MSS/API)
| Specification | Scope |
|---|---|
| ASME B16.11 | Socket weld and threaded forged fittings, NPS 1/8-4”, Class 2000-9000 |
| MSS SP-79 | Insert-type socket-welding fittings from bar stock, NPS 1/2-4” |
| MSS SP-83 | Class 3000 and 6000 threaded and socket-welding pipe unions |
| MSS SP-97 | Integrally reinforced forged branch outlet fittings (Weldolets, Threadolets, Sockolets) |
| API 602 | Compact steel gate, globe, and check valves, NPS 1/8-4” (refinery/petrochemical) |
When specifying forged fittings, match the material grade to the pipe grade, select the class for the design pressure/temperature, and verify the correct specification applies. In practice, ASME B16.11 covers 90% of what you will encounter on small-bore piping in oil and gas or power plant work.
Types of Forged Fittings
Forged fittings are classified two ways: by connection type (socket weld vs. threaded) and by body shape (elbow, tee, coupling, etc.).
Socket Weld vs. Threaded Fittings Types
 Socket weld fitting (left), threaded fitting (right)
Socket weld fitting (left), threaded fitting (right)
Socket Weld Fittings (“SW”)
The pipe slides into the fitting socket and a fillet weld seals the joint. Available in NPS 1/8”-4”, Class 2000-9000.
Socket weld is the go-to connection for small-bore high-pressure work: steam lines, instrument piping on process units, chemical injection. The fillet weld joint is strong, leak-tight, and can be radiographed if required. The downside is labor: welding hundreds of small-bore connections on a plant turnaround is slow and expensive. But for steam, hydrocarbons, toxic fluids, and any service where you cannot tolerate a leak, socket weld is the right choice.
Compared to buttweld fittings, socket weld connections are quicker to fit up (no precise bevel prep needed) and work better in tight spaces. The trade-off is that buttweld joints give a smoother internal bore and better flow characteristics, and they are the only option above NPS 4”.
Remember the 1/16” (1.6mm) expansion gap between pipe end and socket bottom before welding. This is not optional.
 Socket weld fittings (left) vs. Threaded fittings (right)
Socket weld fittings (left) vs. Threaded fittings (right)
Socket-Weld vs. Butt-Weld Fittings
| Aspect | Socket Weld | Butt Weld |
|---|---|---|
| Pipe size | Small bore (up to NPS 4”) | NPS 1/2” and up, typically >2” |
| Weld type | Fillet weld (external) | Full-penetration butt weld |
| Fit-up | Simpler, no bevel needed | Requires precise alignment and bevel prep |
| Internal bore | Slight step at socket | Smooth, continuous |
| Leak risk | Very low (welded joint) | Lowest (full-pen weld, smooth transition) |
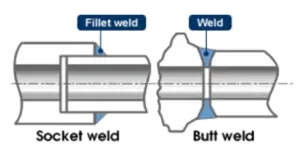
Fillet weld vs. Butt Weld: a butt welding connection fills the gaps between two devices, that are beveled at 30 degrees.
Threaded Fittings (“THD” or “THDD”)
Threaded fittings screw onto the pipe, no welding required. They are the fastest fittings to install and the easiest to disassemble for maintenance. You will find them on utility water, cooling water, fire protection, low-pressure drains, and instrument connections where socket weld is not justified.
The flip side: threaded joints are the weakest link in a piping system. Threads cut into the pipe wall, reducing its effective thickness. They can back out under vibration, and thermal cycling loosens them over time. Never use threaded fittings on lines subject to significant vibration, thermal shock, or hazardous fluid service. Most engineering specs restrict threaded connections to NPS 2” and below, Class 2000 or 3000, in non-critical service.
Available shapes include elbows (45/90 deg), tees (equal/reducing), couplings (full/half/reducing), caps, nipples, unions, and bushings. Materials are the same as socket weld: ASTM A105, A182, A350 in the standard grades.
Types of Threads for Threaded Fittings
The two major thread standards are BSP (55 deg angle) and NPT (60 deg angle). They are not interchangeable; cross-threading BSP into NPT (or vice versa) is a common field mistake that results in leaks and damaged fittings.
BSP Fittings (BSPT/BSPP)
BSP (British Standard Pipe) is the dominant thread standard in the UK, Europe, Asia, and Australia. It comes in two variants:
| Type | Sealing Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BSP Parallel (BSPP) | Bonded or metal seal compressed between mating surfaces | Constant diameter (G-thread); used where a fluid-tight seal is required on the threads’ periphery |
| BSP Tapered (BSPT) | Thread interference (similar to NPT) | Diameter tapers down, providing a tighter seal as threads engage; pressure-tight seal without additional sealing mechanism |
BSPP is common in hydraulic and water systems; BSPT seals by thread interference and is used on pressurized oil and gas piping. Outside North America, BSP fittings are standard stock.
NPT Fittings
NPT (National Pipe Taper) is the North American standard, per ANSI/ASME B1.20.1. The threads taper at 1 deg 47’ per side, so they wedge tighter as you screw them in.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Tapered Threads | Tapered at 1°47’24” (1.7899°) per side; diameter decreases towards the fitting end for interference fit |
| Sealing Mechanism | Achieved through thread deformation when tightened; requires sealant (Teflon tape or pipe dope) |
| Standards | Must conform to ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 specifications |
NPT threads alone do not seal reliably; always use Teflon tape or pipe dope. Over-tightening cracks the fitting body (especially in stainless steel, which galls easily). NPT fittings can be reused if threads are undamaged, but apply fresh sealant every time.
NPT threading is covered by the ASME B1.20.1 specification and is based on 60° thread flank angles (vs. 55° of the BSP type).
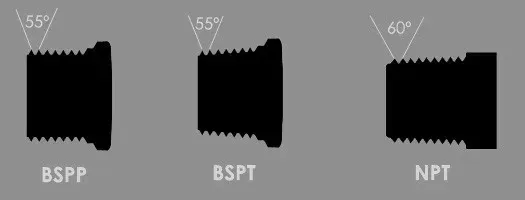 BSP (BSPP/BSPT) vs NPT: thread angle 55 vs 60 Deg.
BSP (BSPP/BSPT) vs NPT: thread angle 55 vs 60 Deg.
Forged Fittings by Shape
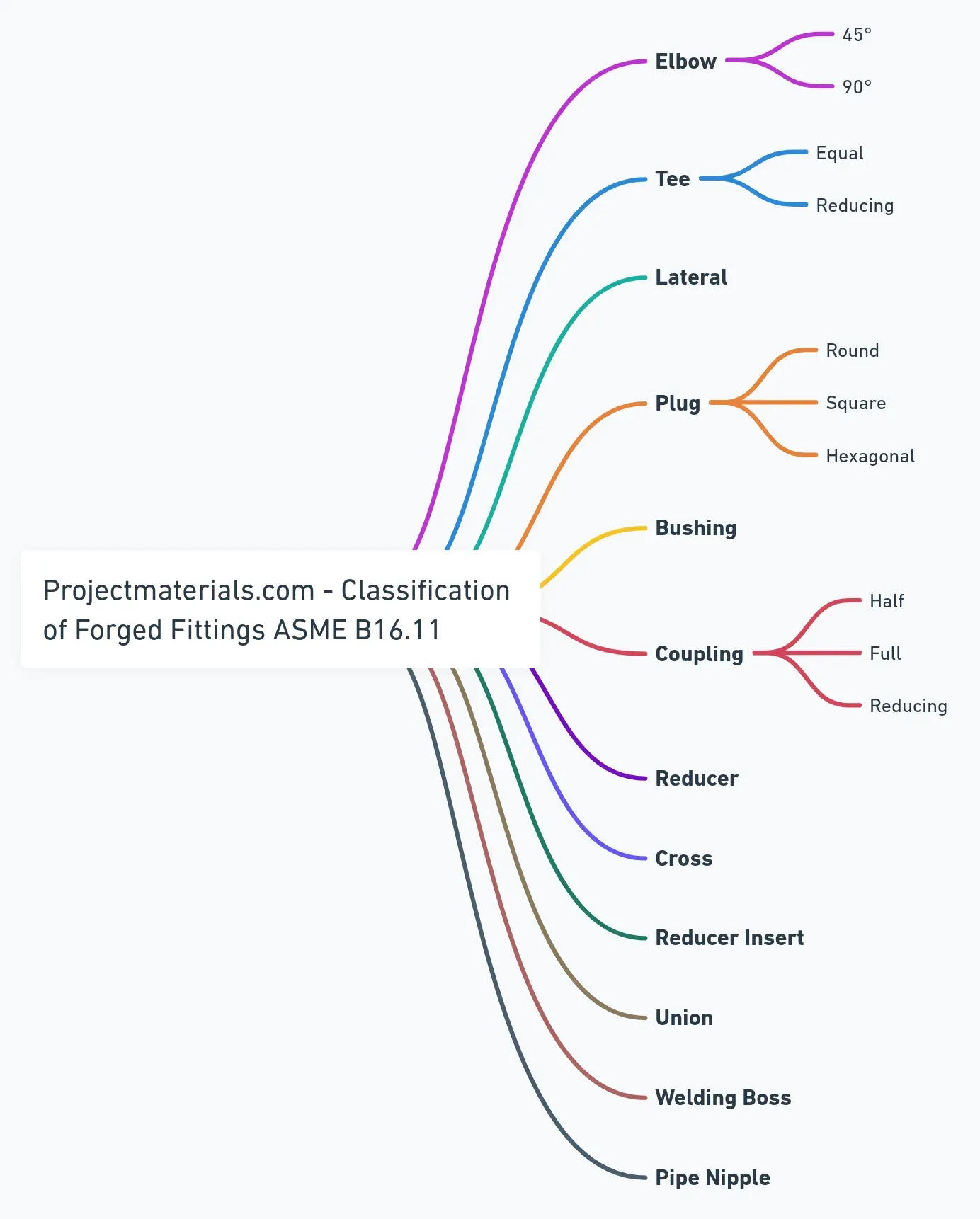 ASME B16.11 Forged Fittings Classification
ASME B16.11 Forged Fittings Classification
Forged Elbow 45/90 Degrees

Forged elbows change the direction of flow. Available in socket weld or threaded, in all standard material grades per ASME B16.11. Three main types:
- 45-Degree Elbow: Makes a gentler turn that produces less pressure drop than a 90. Use these where you can get away with two 45s instead of one 90, as the flow characteristics are noticeably better.
- 90-Degree Elbow: The standard quarter-turn. The most common forged fitting you will order on any project.
- Street Elbow: Has one male end and one female end, so it threads directly into another fitting without needing a nipple. Invaluable in tight spots where you cannot fit an extra piece of pipe between fittings.
Forged Tee (Equal/Reducing)

Forged tees split or combine flow. An equal tee has the same bore on all three ends; a reducing tee has a smaller branch connection. Available with socket weld or threaded connections per ASME B16.11 and MSS SP-75.
Forged Lateral

A forged lateral branches off the main line at 45 degrees (or sometimes 30 degrees) rather than the 90 degrees of a tee. The Y-shape gives much better flow characteristics than a tee branch: lower pressure drop, less turbulence at the junction. You will see laterals specified on drain headers and anywhere the designer wants to minimize erosion at the branch takeoff.
Forged Plug (Round, Squared, Hex)

Forged plugs close off (blind) the end of a fitting, valve, or pipe section. Available in round, square, and hex head configurations. Hex and square heads allow torque with a wrench; round plugs give a flush, clean appearance. You will order dozens of these for hydrotest blanking and dead-end terminations.
Bushings

A forged bushing reduces the bore of a larger fitting, valve, or pipe to accept a smaller pipe. One end has male threads that screw into the larger connection; the other end has female threads for the smaller pipe. Bushings are quick, cheap reducers, though for process piping, most specs prefer a reducing coupling or a proper concentric/eccentric reducer for better flow.
Couplings (Half, Full)

Couplings are the simplest forged fitting: they join two pipes in a straight line.
- Full Coupling: Socket or threaded ends on both sides; joins two pipes of the same diameter.
- Half Coupling: Socket or threaded on one end only, the other end is butt-welded or fillet-welded to a pipe, vessel, or header. Half couplings are commonly used as instrument or branch connections on larger pipe.
- Reducing Coupling: Different bore on each end, connecting two different pipe sizes in line.
Reducers and Reducer Inserts

Forged reducers connect pipes of different diameters. Two types:
- Concentric Reducer: Centerlines aligned, the standard choice for vertical lines and anywhere air/sediment entrapment is not a concern.
- Eccentric Reducer: One side flat (top or bottom aligned). On horizontal lines, install flat-on-bottom (“FOB”) to prevent liquid pockets, or flat-on-top (“FOT”) at pump suctions to prevent vapor pockets.
Reducer Inserts
Reducer inserts slip into the socket of a larger fitting or valve to accept a smaller pipe, an economical, space-saving alternative to a full reducing coupling. ASME B16.11 defines two types:
| Type | Use | Installation |
|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | Flow from larger to smaller bore | Insert sits in the socket; pipe enters through the insert. Gives a smooth internal transition. |
| Type 2 | Flow from smaller to larger bore, or where Type 1 geometry does not suit | Similar installation, but oriented for reverse flow or specific assembly constraints. |
Both types must be carefully aligned in the socket before welding. A misaligned reducer insert creates a step in the bore that traps solids and disrupts flow.
Union

A forged union is a three-piece fitting (male end, female end, and nut) that allows disconnection without cutting pipe. You will find unions wherever maintenance access is needed: at control valves, instruments, and equipment connections that require periodic removal. The nut draws the two halves together with a metal-to-metal or gasket seal.
Unions come in male-to-female, female-to-female, lug-nut, and Rockwood designs. They comply with MSS SP-83.
Welding Boss

A forged welding boss provides a take-off point on a pipe or vessel for instrument connections (pressure gauges, thermowells, level transmitters) or small branch lines. The boss is welded directly to the pipe surface and has a threaded or socket outlet for the instrument or branch connection. You will see welding bosses on every process line that carries instrumentation; they are the standard method for mounting a thermowell or a pressure tap on small-to-medium bore piping.
Swage Nipple
 Swage nipple ASME B16.11
Swage nipple ASME B16.11
A swage nipple (or swage reducer) transitions between two different pipe sizes with a gradual conical taper. Think of it as a short reducer with plain, beveled, or threaded ends on each side. Swage nipples are manufactured by forging or by machining from solid bar stock.
Two configurations:
- Concentric: Uniform taper, centerlines aligned. Standard choice when alignment matters.
- Eccentric: Off-center taper, one side flat. Used on horizontal runs where you need flat-on-bottom for drainage or flat-on-top at pump suctions.
End connections can be plain (for butt welding), threaded (NPT/BSP), or a combination (e.g., one end threaded, the other beveled). Match the material and pressure rating to the connected piping; the swage nipple must be at least as strong as the weakest pipe it joins.
Forged Fittings Materials
Carbon Steel Fittings ASTM A105 (Forged)
ASTM A105 is the standard carbon steel forging for socket weld and threaded fittings. It pairs with ASTM A53, A106, and API 5L pipe in high-temperature service. For low-temperature service (below -29 deg C / -20 deg F), switch to ASTM A350 fittings to match ASTM A333 low-temp pipe.
A105 Forged Fittings Materials, Chemical Composition %
| Material Grade | Grade or Class | C | Si | Mn | S | P | Cu | Ni | Cr | Mo | V | Cb/Nb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM A105 | 0.35 | 0.10-0.35 | 0.60-1.05 | 0.04 | 0.035 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 0.08 | ||
| ASTM A181 | 60 | 0.35 | 0.10-0.35 | 1.1 | 0.05 | 0.05 | ||||||
| 70 | 0.35 | 0.10-0.35 | 1.1 | 0.05 | 0.05 | |||||||
| ASTM A266 | 1 | 0.3 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.40-1.05 | 0.025 | 0.025 | ||||||
| 2 | 0.3 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.40-1.05 | 0.025 | 0.025 | |||||||
| 3 | 0.35 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.80-1.35 | 0.025 | 0.025 | |||||||
| 4 | 0.3 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.80-1.35 | 0.025 | 0.025 | |||||||
| ASTM A350 | LF1 | 0.3 | 0.15-0.30 | 0.60-1.35 | 0.04 | 0.035 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.02 |
| LF2-1 | 0.3 | 0.15-0.30 | 0.60-1.35 | 0.04 | 0.035 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.02 | |
| LF2-2 | 0.3 | 0.15-0.30 | 0.60-1.35 | 0.04 | 0.035 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.02 | |
| LF3-1 | 0.2 | 0.20-0.35 | 0.9 | 0.04 | 0.035 | 0.4 | 3.30-3.70 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.02 | |
| LF3-2 | 0.2 | 0.20-0.35 | 0.9 | 0.04 | 0.035 | 0.4 | 3.30-3.70 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.02 | |
| LF5-1 | 0.3 | 0.20-0.35 | 0.60-1.35 | 0.04 | 0.035 | 0.4 | 1.00-2.00 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.02 | |
| LF5-2 | 0.3 | 0.20-0.35 | 0.60-1.35 | 0.04 | 0.035 | 0.4 | 1.00-2.00 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.02 | |
| LF6-1 | 0.22 | 0.15-0.30 | 1.15-1.50 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 0.04-0.11 | 0.02 | |
| LF6-2 | 0.22 | 0.15-0.30 | 1.15-1.50 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 0.04-0.11 | 0.02 | |
| LF6-3 | 0.22 | 0.15-0.30 | 1.15-1.50 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 0.04-0.11 | 0.02 | |
| LF9 | 0.2 | 0.40-1.06 | 0.04 | 0.035 | 0.75-1.25 | 1.60-2.24 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.02 | ||
| LF787-2 | 0.07 | 0.4 | 0.40-0.70 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 1.00-1.30 | 0.70-1.00 | 0.60-0.90 | 0.15-0.25 | 0.03 | 0.02 min | |
| LF787-3 | 0.07 | 0.4 | 0.40-0.70 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 1.00-1.30 | 0.70-1.00 | 0.60-0.90 | 0.15-0.25 | 0.03 | 0.02 min |
A105 Forged Fittings, Mechanical Properties
| Material Grade | Grade or Class | Tensile Strength min, Ksi | Yield Strength Ksi @ 0.2% | Elongation in 2 in, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM A105 | - | 70 | 36 | 22 |
| ASTM A181 | 60 | 60 | 30 | 22 |
| ASTM A181 | 70 | 70 | 36 | 18 |
| ASTM A266 | 1 | 60-85 | 30 | 23 |
| ASTM A266 | 2 | 70-95 | 36 | 20 |
| ASTM A266 | 3 | 70-95 | 36 | 20 |
| ASTM A266 | 4 | 75-100 | 37.5 | 19 |
| ASTM A350 | LF1 | 60-85 | 30 | 25 |
| ASTM A350 | LF2-1 | 70-95 | 36 | 22 |
| ASTM A350 | LF2-2 | 70-95 | 36 | 22 |
| ASTM A350 | LF3-1 | 70-95 | 37.5 | 22 |
| ASTM A350 | LF3-2 | 70-95 | 37.5 | 22 |
| ASTM A350 | LF5-1 | 60-85 | 30 | 25 |
| ASTM A350 | LF5-2 | 70-95 | 37.5 | 22 |
| ASTM A350 | LF6-1 | 66-91 | 52 | 22 |
| ASTM A350 | LF6-2 | 75-100 | 60 | 20 |
| ASTM A350 | LF6-3 | 75-100 | 60 | 20 |
| ASTM A350 | LF9 | 63-88 | 46 | 25 |
| ASTM A350 | LF787-2 | 65-85 | 55 | 20 |
| ASTM A350 | LF787-3 | 75-95 | 65 | 20 |
Low-Alloy Steel Fittings ASTM A182 (Forged)
Low-alloy forged fittings match chrome-moly ASTM A335 pipes: P5/F5, P9/F9, P11/F11, P22/F22, P91/F91. Always keep the fitting grade consistent with the pipe grade. Mixing, say, F11 fittings on P22 pipe is a common procurement error that creates a weak point in the system.
| Low-Alloy Forged Fittings Materials | A182 F5 | A182 F9 | A182 F11 | A182 F22 | A182 F91 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 0.15 Max | 0.15 Max | 0.10-0.20 (2) | 0.05-0.15 | 0.08-0.12 |
| Mn | 0.30-0.60 | 0.30-0.60 | 0.40-0.65 | 0.30-0.60 | 0.30-0.60 |
| P | 0.035 Max | 0.030 Max | 0.025 Max | 0.035 Max | 0.020 Max |
| S | 0.030 Max | 0.030 Max | 0.040 Max | 0.040 Max | 0.010 Max |
| Si | 0.50 Max | 0.50-1.00 | 0.50-0.80 | 0.50 Max | 0.20-0.50 |
| Ni | 0.50 Max | - | - | 0.40 Max | |
| Cr | 4.0-6.0 | 8.0-10.0 | 1.00-1.50 | 2.00-2.50 | 8.0-9.5 |
| Mo | 0.44-0.65 | 0.90-1.10 | 0.44-0.65 | 0.90-1.10 | 0.85-1.05 |
| V | - | - | - | 0.18-0.25 | |
| Cu | - | - | - | - | |
| Other | - | - | - | Cb, 0.06-0.10; N, 0.03-0.07; Al, 0.04 max. |
Stainless Steel Fittings ASTM A182 (Forged)
Stainless steel forged fittings match ASTM A312 pipes. The most commonly specified grades are F304/F304L and F316/F316L. For high-temperature service, use the “H” grades (F304H, F316H) which have controlled carbon ranges for creep resistance.
ASTM A182 Forged Fittings Materials, Chemical Composition %
| A182 Grade | C | Mn | P | S | Si | Ni | Cr | Mo | Nb | Ti | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F304(1) | 0.08 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 8.0-11.0 | 18.0-20.0 | ||||
| F304H | 0.04-0.10 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 8.0-11.0 | 18.0-20.0 | ||||
| F304L(1) | 0.030 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 8.0-13.0 | 18.0-20.0 | ||||
| F304N(2) | 0.08 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 8.0-10.5 | 18.0-20.0 | ||||
| F304LN(2) | 0.030 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 8.0-10.5 | 18.0-20.0 | ||||
| F309H | 0.04-0.10 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 12.0-15.0 | 22.0-24.0 | ||||
| F310 | 0.25 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 19.0-22.0 | 24.0-26.0 | ||||
| F310H | 0.04-0.10 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 19.0-22.0 | 24.0-26.0 | ||||
| F310MoLN | 0.030 | 2.0 | 0.030 | 0.015 | 0.40 | 21.0-23.0 | 24.0-26.0 | 2.0-3.0 | N 0.10-0.16 | ||
| F316 | 0.08 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 10.0-14.0 | 16.0-18.0 | 2.0-3.0 | |||
| F316H | 0.04-0.10 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 10.0-14.0 | 16.0-18.0 | 2.0-3.0 | |||
| F316L(1) | 0.030 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 10.0-15.0 | 16.0-18.0 | 2.0-3.0 | |||
| F316N(2) | 0.08 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 11.0-14.0 | 16.0-18.0 | 2.0-3.0 | |||
| F316LN(2) | 0.030 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 11.0-14.0 | 16.0-18.0 | 2.0-3.0 | |||
| F316Ti | 0.08 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 10.0-14.0 | 16.0-18.0 | 2.0-3.0 | (3) | N 0.10 max | |
| F317 | 0.08 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 11.0-15.0 | 18.0-20.0 | 3.0-4.0 | |||
| F317L | 0.030 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 11.0-15.0 | 18.0-20.0 | 3.0-4.0 | |||
| F321 | 0.08 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 9.0-12.0 | 17.0-19.0 | (4) | |||
| F321H | 0.04-0.10 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 9.0-12.0 | 17.0-19.0 | (5) | |||
| F347 | 0.08 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 9.0-13.0 | 17.0-20.0 | (6) | |||
| F347H | 0.04-0.10 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 9.0-13.0 | 17.0-20.0 | (7) | |||
| F348 | 0.08 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 9.0-13.0 | 17.0-20.0 | (6) | Co 0.20Ta 0.10 | ||
| F348H | 0.04-0.10 | 2.0 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 9.0-13.0 | 17.0-20.0 | (7) | Co 0.20Ta 0.10 |
Forged fittings are also available in duplex (ASTM A182 F51), super duplex (F53/F55), and various nickel alloys (Inconel, Incoloy, Monel, Hastelloy) for severe corrosion or extreme temperature service.
Forged Fittings Manufacturers
- Anvil/JB Smith
- Beck
- Bonney Forge
- Del Corte
- General Plug and Manufacturing
- IML/OMC
- Interfit Vallourec
- Lame Fittings
- Jefferson Union
- Mega Mex
- M.E.G.A.
- Mueller Industries
- Nicholson
- Penn Machine
- Phoenix/Capitol
- Ulma
- Ward
- Westbrook
- WFI
- Viar
Leave a Comment
Have a question or feedback? Send us a message.
Previous Comments
Hi , I'm looking for the following prices . 25mm threaded socket working pressure 10bar and threaded 25mm nipples all carbon steel .
Dear Sirs, For a special application I am looking for one(1) piece of: Y-Filter,socket weld,1/2",B16.11 with IPS thread delivered Istanbul-Turkey. my best regards, Nejat Uner Istanbul-Turkey
Hi, I have used threaded fittings for steam network then found later that this type of fittings is not reliable for steam application so I have decided to weld around the fittings. Is this OK?
ELBOW:90 DEG; 1 INCH ONE END MALE & ONE END FEMALE NPT THREAD, F316; ASTM A182, FORGED TYPE 3000 LBS. Qty: 32 pcs PLEASE QUOTE PRICES IN CIF SINGAPORE.
Great post to share. very informative content
2) SP97 A105 SA105N 57008 6-1 ½” x 3/4 6M (Sch 160) BONNY SP97 (B16.11) What does 57008 mean
Dear Sir, Greetings. Please quote your best price and delivery time for the below item: SK2022030303 – 30 DAYS VALIDITY REQUIRED – LOWEST OFFER TO BE QUOTED – AS PER QP AML – BCD : 07/03/2022 Note 1) Quoted items should be exactly as per specification. If any deviation to be highlighted separately. 2) MTC 3.1 only required. 3) Sea worthy packing cost & attested shipping document cost to be quoted separately. 4) Manufacturer name and origin to be mentioned against each line items 5) Ex-work packed basis quote required. 6) All pipes / fittings / flanges / plates shall be manufactured within 5 years prior to collection or delivery 7) Please provide catalogue / datasheet for the item to be quoted. 8) As per QP AML Material Description: 00002 10096734 QTY: 30 Piece 24.MAR.2022 NIPPLE,PIPE,HEX,1/4IN,MI,GALV,, NIPPLE,PIPE SH_NAME NIPPLE,PIPE NIPPLE_TYPE HEX NIPPLE_DIMENSIONS 1/4IN NIPPLE_MATL MI NIPPLE_FINISH GALV NIPPLE_PRESS_RTG 25 BAR AT -20 TO 120 DEGC NIPPLE_CONN_DATA NPT-M EQUAL NIPPLE_INSPECTION_CERT ISO 10474-2.1 NIPPLE_DESIGN_SPEC BS 143 NIPPLE_MATL_SPEC ASTM A197M NIPPLE_COATING_SPEC ASTM A153 CL A Inspection text Certificate of Compliance BS EN 10204 / ISO 10474 type 2.1 Your offer the earliest is highly appreciated. Waiting for your prompt reply. Thanks & Regards, Heinlyn Inside Sales Representive – Oil & Gas Division BECON TRADING & CONTRACTING W.L.L Building No: 94, D-Ring Road, Street-250, Zone 42, Al-Hilal Area, PO Box #37312, Doha, Qatar [email protected]
Dear Sir/Madam, Yancheng Xinfujit Machinery Co.,Ltd. is a manufacturer specialized in hydraulic flange and fittings for a variety of hose,pipe and tube assemblies,The products widely used in petrol, the chemiacal industry, construction machinery and equipment. Support for the hydraulic piping system. Our Product group of SAE Flange including: SAE Split flanges SAE flange clamps SAE weld flanges SAE Butt weld flanges SAE socket weld flanges SAE socket weld elbow flanges SAE threaded flanges/SAE threaded counter flanges SAE BSPP threaded flanges SAE NPT threaded flanges SAE closed flanges/SAE Blind flanges SAE blocks All the above products of SAE flanges come in two main series 3000 psi standard pressure series, designed according to standard ISO 6162-1, this is also called code 61 flanges 6000 psi high pressure series, designed according to standard ISO 6162-2, this is also called code 62 flanges. Materials of SAE hydraulic flanges Carbon steel:C45,C20,CQ235 or on requests. Stainless steel:304,304L,316 and 316L or equivalent EN/DIN stainless steel grades,used for connecting stainless steel hydraulic tubing. other materials also can be supplied on request with some required min. order quantity. Our products export to more than 30 countries, and get well reputation. We have our own export licence. We are looking forward to cooperating with you sincerely. Looking forward to hearing from you. Best regards Eileen Jia Yancheng Xinfujit Machinery Co.,Ltd. Mobile:00 86 18262378752(wechat) Fax:00 86 515 86523666 Contact person:Eileen Jia Website: https://xfjt168.en.alibaba.com/ E-mail:[email protected] Address:No.8 2# Road Private Industrial Park Jianhu County, Yancheng city,Jiangsu Province,China.
Good work! Thank you for your participation. Look into it as well. Shree Impex Alloys, Stainless Steel Seamless Pipe Manufacturer in India, Stainless Steel Seamless Pipe, Stainless Steel Seamless Pipe Manufacturer, Stainless Steel Seamless Tube Manufacturer in India and Stainless Steel Welded Pipe Manufacturer in India.