Forged vs Seamless Pipes Compared

Forged Vs. Seamless Pipe
What Is a Forged Pipe?
Definition
A forged pipe is manufactured by forging, a process that shapes metals through localized compressive forces. The term “forged” refers to the manufacturing method, not to the shape or application of the pipe.
 forged pipe
The forging process involves heating a metal piece, then hammering or pressing it into the desired shape. For pipes, the process starts with a cylindrical billet that is pierced to create a hollow center, similar to the initial steps of seamless pipe manufacturing. The difference is in the subsequent steps, where the metal is mechanically worked (CNC machined) to achieve the final dimensions and properties.
forged pipe
The forging process involves heating a metal piece, then hammering or pressing it into the desired shape. For pipes, the process starts with a cylindrical billet that is pierced to create a hollow center, similar to the initial steps of seamless pipe manufacturing. The difference is in the subsequent steps, where the metal is mechanically worked (CNC machined) to achieve the final dimensions and properties.
Manufacturing Process of Forged Pipes
The main production steps for forged seamless pipes are depicted below:
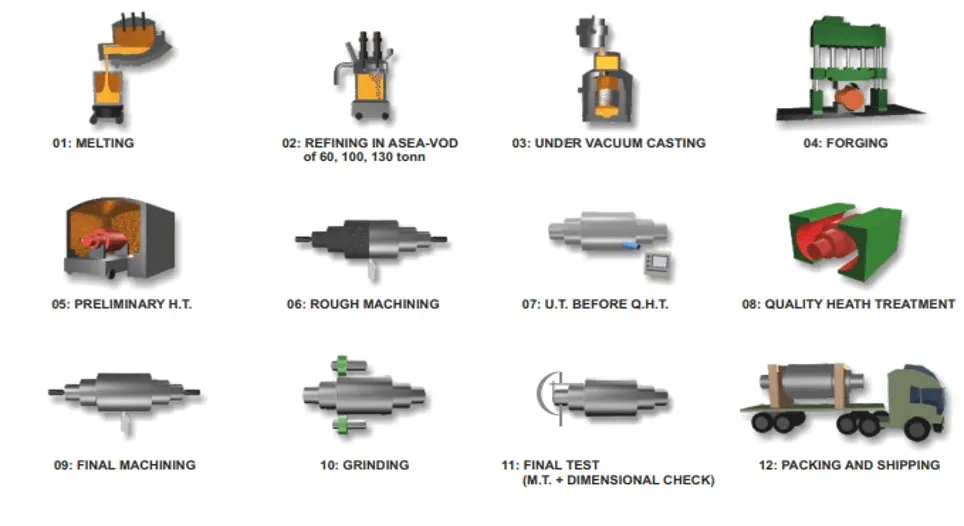 manufacturing process forged pipe
manufacturing process forged pipe
| Step | Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Billet Preparation | Produce solid cylindrical billets cut to desired length |
| 2 | Billet Heating | Heat billets to reduce yield strength and enable plastic deformation |
| 3 | Forging | Apply compressive forces to shape billets into cylindrical pipe forms |
| 4 | Piercing | Create hollow tube with uniform inner diameter |
| 5 | Rolling and Sizing | Elongate and reduce diameter to achieve desired dimensions and wall thickness |
| 6 | Heat Treatment | Relieve stresses, refine grain structure, enhance mechanical properties |
| 7 | Machining | Achieve final dimensions, surface finish, and tolerances |
| 8 | Testing and Inspection | Verify quality and conformance to specifications |
| 9 | Finishing and Packaging | Clean, finish, and package for shipping |
Billet Preparation
The process begins with solid cylindrical billets of steel or other suitable materials, typically produced by continuous casting or hot rolling, and cut to the required length.
Billet’s Heating
The billets are heated to high temperatures in a controlled atmosphere furnace to increase malleability. Heating reduces the material’s yield strength and allows plastic deformation during forging.
Forging
The heated billets are placed under a forging hammer or press and deformed into cylindrical shapes through compressive forces. Forging may be performed in multiple stages to reach the target dimensions and mechanical properties.
Piercing
After forging, the rough blanks are pierced to create a hollow tube with a uniform inner diameter. The blanks are forced through dies and rollers to remove excess material and form the inner surface.
Rolling and Sizing
The pierced blanks are elongated and reduced in diameter through a series of rolling passes until the target dimensions and wall thickness are reached. Hot or cold rolling may be used depending on the material and specifications.
Heat Treatment
Once formed and sized, the pipes undergo heat treatment (annealing or tempering) to improve mechanical properties and microstructure. Heat treatment relieves internal stresses, refines grain structure, and improves strength, toughness, and ductility.
Machining
After heat treatment, the pipes undergo machining operations (turning, boring, threading) to reach final dimensions, surface finish, and tolerances. Machining removes surface defects and ensures dimensional accuracy.
Testing and Inspection
Throughout production, forged pipes are tested and inspected for quality and specification conformance. Non-destructive methods include ultrasonic testing, eddy current testing, and visual inspection; destructive methods include tensile testing and hydrostatic testing.
Finishing and Packaging
After passing all quality checks, the pipes are finished, cleaned, and packaged for shipment.
In summary, forged pipe production combines forging and machining techniques to produce seamless pipes with controlled mechanical properties and tight dimensional tolerances.
The picture below represents a forging press of approximately 12.000 tons:
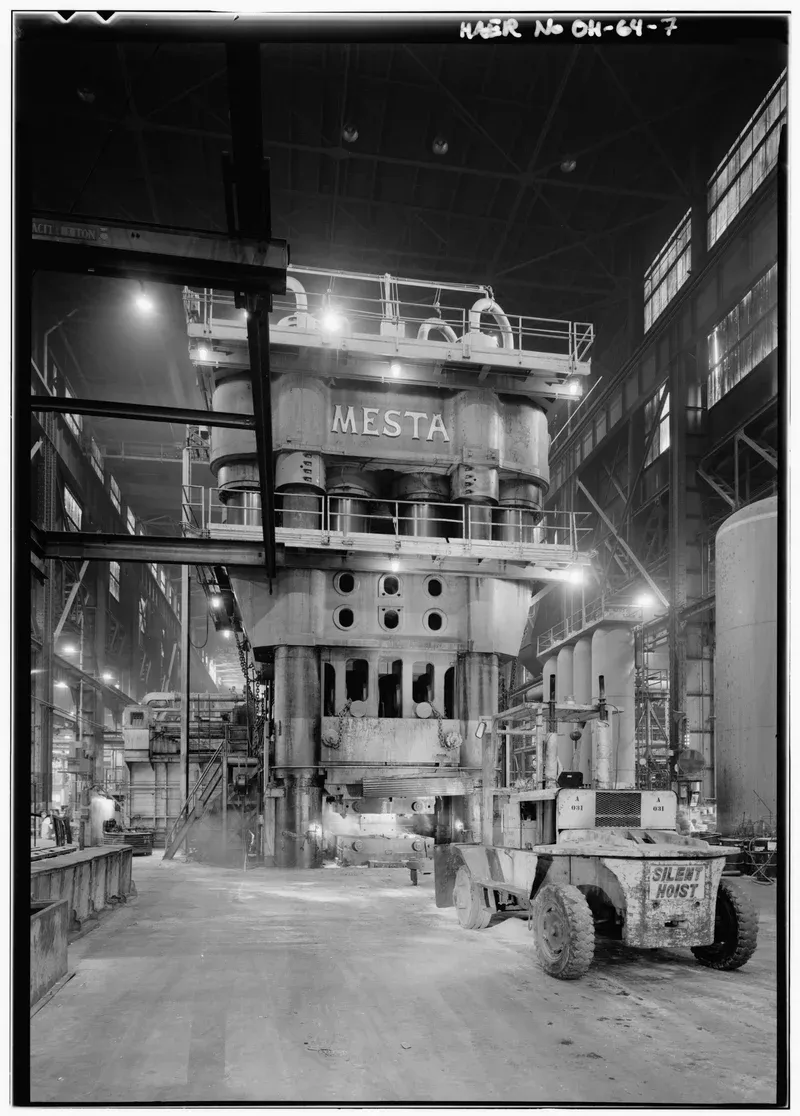 Industrial forging press (approx. 50,000 tons capacity)
Industrial forging press (approx. 50,000 tons capacity)
Features of Forged Pipes
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Strength | Forging refines the grain structure and aligns it to the pipe shape, producing uniform composition and superior strength and fatigue resistance compared to cast or machined parts. |
| High Durability | No seams means no weak points. Forged pipes withstand extreme internal pressures and harsh environmental conditions. |
| Customizability | Forged pipes can be tailored to specific sizes and shapes, with more flexibility than casting or extrusion. |
| Superior Reliability | The homogenous structure reduces the risk of hidden defects (voids, inclusions) that can cause failure under stress. |
| Chemical Resistance | The absence of seams and uniform structure improve chemical resistance, as there are no preferential corrosion paths. |
| Thermal Stability | Forged pipes maintain structural integrity across a wide temperature range, making them suitable for high-temperature service. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Without welds or seams that are prone to preferential attack, forged pipes perform better in corrosive environments than welded alternatives. |
Elective Applications of Forged Pipes
| Application | Why Forged Pipes Are Preferred |
|---|---|
| High-Pressure Applications | Systems operating under high internal pressures, such as hydraulic circuits. |
| Oil and Gas Industry | Drilling and transport lines requiring high strength and pressure resistance. |
| Power Generation | Steam lines and other high-consequence piping within power plants. |
| Chemical Processing | Process piping exposed to corrosive substances and elevated temperatures. |
| Marine Applications | Offshore piping requiring both strength and corrosion resistance in seawater exposure. |
| Nuclear Industry | Nuclear plant piping where reliability and strict tolerance control are mandatory. |
What Is a Seamless Pipe?
A seamless pipe has no welded joints or seams. It is produced by drawing a solid billet over a piercing rod to create a hollow shell.
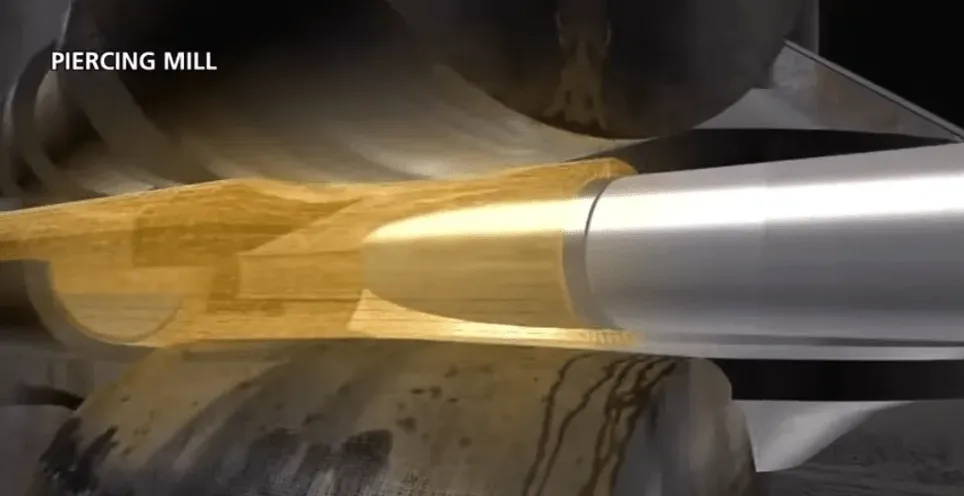

Piercing mill seamless pipes
The production process of seamless pipes is fully automated and mainly oriented to standard sizes and large quantities (an order could go from a minimum quantity of 20 pipes to a pipeline order with 5.000 km / 450 pipes of the same size). Pipes are not mechanically CNC machined except for the ends (pipe ends are beveled or threaded to allow connection of each pipe).
The manufacturing process of a seamless pipe can be outlined as follows:
| Step | Process | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Heating of the Billet | A solid round steel billet is heated at a high temperature to make it pliable. |
| 2 | Piercing | Once the billet is heated enough, it is pierced through the center using a piercer to create a hollow shell. This is often done on a rotary piercing mill where the billet is fed between rollers and a mandrel (piercing rod) to start the hollowing process. |
| 3 | Rolling | The hollow shell is then elongated and rolled to give it the desired thickness and diameter. This is usually achieved using a series of rolling mills, which may include a mandrel mill and plug mill. In the mandrel mill, a mandrel bar is inserted into the tube and the assembly is then rolled until the desired dimensions are achieved. |
| 4 | Sizing | After rolling, the tube may be further processed to achieve the precise size and tolerances required. This can include additional passes through a reducer mill and sizing mill. |
| 5 | Heat Treatment | To achieve the desired mechanical properties, the pipe is then subjected to heat treatment such as annealing or quenching and tempering. |
| 6 | Finishing | Finally, the pipe undergoes finishing steps, which may include cutting, straightening, inspecting, and sometimes further machining. |
Learn more about seamless pipes and their manufacturing process.
Seamless pipes are used where strength under extreme pressure is required: oil and gas, chemical plants, power generation, and machinery components. They handle greater stress than welded pipes, which have a seam that can be a weak point under pressure and temperature cycling.
Differences Between Forged and Seamless Pipes
Dimensional Parameters
| Parameter | Forged Pipe | Seamless Pipe |
|---|---|---|
| Defined by | Outside Diameter (OD) + Inside Diameter (ID) | Outside Diameter (OD) + Wall Thickness (WT) |
| Control type | ID-controlled | OD-controlled |
| Also known as | ”Minimum Wall Thickness Pipes” (minimum thickness guaranteed) | “Average Wall Thickness Pipes” |
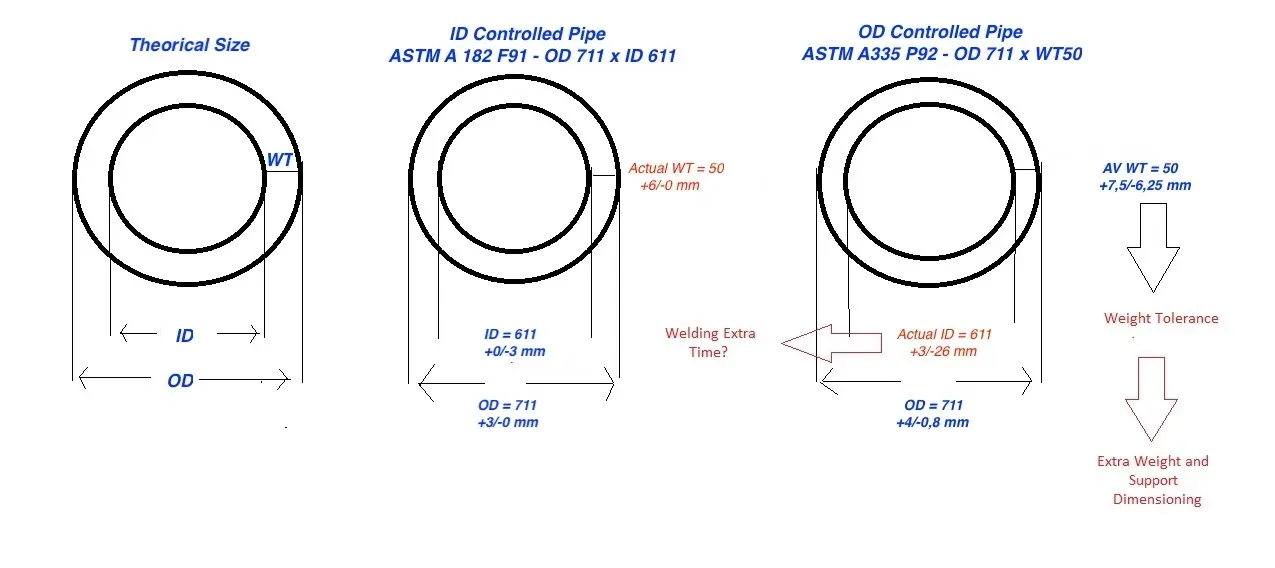 Forged vs seamless pipe dimensions
Seamless pipes are also called “OD-controlled pipes” or “Average Wall Thickness Pipes”. The theoretical size of each pipe is different from the actual one (due to limitations in production, and the international norms allowing some dimensional tolerances). For example, in an OD-controlled size OD711 mm x WT 50 mm, the actual ID might show a 25 mm difference from the ordered (= theoretical) one.
Forged vs seamless pipe dimensions
Seamless pipes are also called “OD-controlled pipes” or “Average Wall Thickness Pipes”. The theoretical size of each pipe is different from the actual one (due to limitations in production, and the international norms allowing some dimensional tolerances). For example, in an OD-controlled size OD711 mm x WT 50 mm, the actual ID might show a 25 mm difference from the ordered (= theoretical) one.
This size difference (actual vs. theoretical) might generate unexpected costs and delays during installation at the site. The welding of two pipes with different IDs might require longer time or extra machining of pipe ends (that were not accounted for during the pipework engineering process).
Imperfect welding might be very critical in offshore applications or for pipes installed within a power plant, as high-temperature steam might generate unwanted vortex movements, cavitation, and creep problems to all the ancillary utilities existing in the plant.
Cost-Effectiveness
Theoretically, a forged pipe could be produced in any desired size. The question is: when is it better to go for a forged vs. a seamless pipe?
In general, forged pipes are more cost-efficient, compared to seamless pipes, in the following cases and applications:
| Factor | Forged Pipe Advantage |
|---|---|
| Larger OD | Forged pipes show an overall cost advantage for larger OD pipes, say OD > 18” as a rule of thumb |
| Heavier wall thickness | Forged pipes are the elective choice for applications that require heavy wall thickness pipes, for example from 40/50 mm WT upwards |
| Special tolerances or surface finishing | Due to its fine manufacturing process, forged pipes can be produced to custom dimensions and precise tolerances (whereas seamless pipes show a constant divergence between actual vs. theoretical sizes) |
| Small production lots | The minimum order size for a forged mill is just 1 pipe, whereas seamless pipes manufacturers have minimum lot quantities of several tons, generally above 10 |
On the contrary, Seamless Pipes are more cost-efficient in the following cases:
| Factor | Seamless Pipe Advantage |
|---|---|
| Standard OD sizes | Sizes from 12,7 mm (1/2”) to 457 mm (18”) |
| Standard wall thickness | Projects requiring pipes with standard wall thickness, for example below 25/30 mm |
| Large lots | Minimum order is 200 meters / 20 pipes per size |
The image below shows the competitive range for forged pipes (vs. seamless pipes) in terms of pipe OD (outside diameter) and WT (wall thickness):
 forged pipes competitive range
forged pipes competitive range
Typical Cases of Application
Forged seamless pipes are used across multiple industries. The table below lists the most common applications:
| Industry | Applications | Why Forged Pipes Are Used |
|---|---|---|
| Oil and Gas | Drilling operations, well completion, pipeline construction, transmission of crude oil, natural gas, and refined petroleum products | Withstand high-pressure, corrosive environments, and extreme temperatures in upstream, midstream, and downstream operations |
| Petrochemical and Chemical | Reactors, heat exchangers, distillation columns, process equipment | Resistance to chemical corrosion and high temperatures when conveying chemicals, acids, and corrosive fluids |
| Power Generation | Boilers, steam turbines, condensers, heat recovery systems | Transport steam, water, and other fluids at high temperatures and pressures in thermal power plants, nuclear reactors, and renewable energy installations |
| Aerospace and Defense | Aircraft components, missile systems, military vehicles, hydraulic systems, fuel lines | Lightweight yet strong materials with high fatigue resistance for structural components |
| Mechanical and Automotive | Shafts, axles, gears, exhaust systems, suspension components, drivetrain assemblies | Superior strength and durability for high-performance precision components |
| Infrastructure and Construction | Bridges, buildings, tunnels, offshore structures, piling, foundation works | High load-bearing capacity and corrosion resistance |
| Mining and Exploration | Drilling rigs, wellbore casing, pumping systems, mineral processing plants | Drilling, extraction, and transportation of minerals, ores, and fluids |
| Marine and Offshore | Offshore drilling, production platforms, subsea pipelines | Withstand harsh marine environments, high pressures, and corrosive seawater conditions |
Advantages of Forged vs. Seamless Pipes
Forged pipes have several advantages over seamless pipes, particularly for high-strength and high-reliability applications:
Technical Reasons
High-Pressure Tolerance
Forged pipes are preferred in high-pressure applications. The forging process aligns the grain structure to the pipe shape, increasing resistance to internal pressure.
Improved Mechanical Properties
Forging refines the metal’s microstructure and closes porosity, resulting in better strength, ductility, and toughness. This makes forged pipes well-suited for heavy-duty service.
Chemical Consistency
Forging produces a more homogeneous material with consistent chemical properties throughout the cross-section, which is important for chemical and nuclear industry applications.
Reduced Chance of Defects
Forged pipes are made from a single piece of metal shaped under high pressure, with no welding or seams. This reduces the likelihood of defects such as inclusions, voids, or weak spots that could fail under stress.
Durability in Fluctuating Conditions
Forged pipes typically exhibit excellent fatigue resistance and long-term durability, even in applications where the temperature or pressure may fluctuate significantly.
Custom Alloys
Forging allows the production of pipes from alloys that may not be feasible with standard seamless manufacturing methods, which matters for applications requiring non-standard material properties.
Commercial Reasons
Customization and Sizes
Forged pipes can be produced to custom sizes and thicknesses, which is useful when standard pipe dimensions do not meet project requirements.
Cost-Effectiveness for Small Quantities
For small batch sizes, forged pipes are more cost-effective than seamless pipes because the minimum order quantity is lower (as few as 1 pipe vs. 20+ for seamless).
Where these attributes matter, forged pipes are the preferred option, particularly in oil and gas, power generation, and nuclear energy.
Summing Up
Heavy wall-thickness forged pipes are used in more demanding applications than conventional seamless pipes:
- Power Generation steam lines, for instance, require high chrome content (alloy grade 11, grade 22, grade 91, grade 92) and heavy wall thickness lines to resist the high temperatures generated by the energy production process.
- A controlled ID Diameter pipe allows better dimensioning during the engineering stage, reduces welding costs during pipe installation, and furthermore reduces vortex fluid movements & creep risks inside the piping of the plant.
- Offshore parts subject to High Mechanical Stress like Risers, J-Lay Collars, and Spool Pieces are supplied in X grades (X60/X70). Those parts require high mechanical properties, in particular very high tensile strength at low temperatures (for example: an expected crush with the offshore pipeline could create serious damage to the pipelines) and require very strict machining tolerances (for example: pipelines need to be clean with pigs on a routine basis).
- Another common application of forged pipes is for OCTG Couplings in Upstream applications (for example: couplings for OCTG casing pipes size 18 5/8”) for heavy dimensions & heavy thickness that cannot be produced by using the standard seamless production process.
Some examples of forged steel products for application in the oil & gas, power generation, and heavy manufacturing industries:
 Forged J-Lay Collars
Forged J-Lay Collars
 Forged Y-Pieces
Forged Y-Pieces
 Forged Spool Pieces
Forged Spool Pieces
 Forged Riser
Forged Riser
Manufacturers of Forged Pipes
The forged pipes market is a niche segment populated by a large number of small and medium-sized manufacturers.
The world’s most qualified forgings mills are located in Northern Italy (more than 20 suppliers) and Germany, along with some smaller production sites in China.
For Seamless Pipes, we have identified 2 categories of manufacturers (depending on the steel grade family):
| Steel Grade Family | Major Manufacturers | Market Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon steel pipes | Tenaris, Vallourec, Sumitomo | Global groups dominate supply; Chinese manufacturers play a smaller role. USA, Saudi Arabia, and Russia see a strong presence of local suppliers with sales limited to their local markets |
| Stainless steel pipes | Salzgitter DMV, Tubacex, Sandvik | European manufacturers share the market with growing Chinese competition |
Here is a list of global-scale manufacturers (multinational companies) known for producing forged steel pipes:
| Manufacturer | Origin | Industries Served |
|---|---|---|
| Vallourec | France | Oil and gas, power generation, petrochemicals |
| Tubos Reunidos | Spain | Oil and gas, energy, mechanical applications |
| Nippon Steel Corporation | Japan | Offshore and onshore oil and gas |
| TMK Group | Russia | Drilling, exploration, and production (oil and gas) |
| Tenaris | Argentina/Luxembourg | Oil and gas drilling, refining, transportation |
| Borusan Mannesmann | Turkey | Energy, construction, automotive, industrial |
| JFE Steel Corporation | Japan | Oil and gas, mechanical engineering, automotive |
| United States Steel Corporation (U.S. Steel) | USA | Energy, infrastructure, construction |
| Sandvik AB | Sweden | Oil and gas, chemical, aerospace |
| Ovako Group | Europe | Automotive, mining, construction |
This list is not exhaustive. Availability of specific products varies by region and market demand.
Please contact us in case you need recommendations based on steel grade, size, and pipe weight.
ASTM Material Grades Forged vs. Seamless Pipes
The table below shows the most common material grades of seamless pipes and their forged equivalent:
| MATERIAL TYPE | SMLS PIPE GRADE | FORGED GRADE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS - Carbon Steel - High Temperature | ASTM A106 gr B / A53 gr B / API 5L gr B/X42 PSL1 | ASTM A105 | |
| CS - Carbon - Low Temperature | ASTM A 333 gr 6 | ASTM A350LF2 | |
| CS - Carbon Steel | API 5L gr B / X42 PSL1 | ||
| CS - Carbon Steel | API 5L gr B / X42 PSL2 | A694 F42 | |
| CS - Carbon Steel | API 5L gr X42 PSL2 | ||
| CS - Carbon Steel | API 5L gr X52 PSL1 | ||
| CS - Carbon Steel | API 5L gr X52 PSL2 | ASTM A694 F52 | |
| CS - Carbon Steel | API 5L gr X65 PSL1 | ||
| CS - Carbon Steel | API 5L gr X65 PSL2 | A694 F65 | |
| CS - Carbon Steel - Galvanized | ASTM A 53 gr. B | ASTM A105 | |
| AS - Alloy | ASTM A 335 P11 | ASTM A182 F11 | |
| AS - Alloy | ASTM A 335 P22 | ASTM A182 F22 | |
| AS - Alloy | ASTM A 335 P5 | ASTM A182 F5 | |
| AS - Alloy | ASTM A 335 P9 | ASTM A182 F9 | |
| AS - Alloy | ASTM A 335 P91 | ASTM A182 F91 | |
| SS - Stainless | ASTM A 312 TP304-304L | ASTM A182 F304-F304L | |
| SS - Stainless | ASTM A 312 TP316-316L | ASTM A182 F316-F316L | |
| SS - Stainless | ASTM A 312 TP321 | ASTM A182 F321 | |
| SS - Duplex 22 | ASTM A790 UNS S31803 | ASTM A182 F51 | |
| SS - Superduplex 25 | ASTM A790 UNS S32750 / 32760 | ASTM A182 F53 / F55 | |
| SS - Inconel - Nichel Alloy 6625 | ASTM B444 UNS N06625 | ASTM B564 UNS N06625 | |
| SS - Inconel - Nichel Alloy 8825 | ASTM B423 UNS N08825 | ASTM B564 UNS N08825 | |
| CUNI - Cupronickel (CuNi 90/10) | ASTM B466 UNS C70600 | UNS C70600 | |
| CUNI - Cupronickel (CuNi 70/30) | ASTM B466 UNS C71500 | UNS C71500 |
Conclusion
Forged steel pipes are used across many industries for transporting fluids, gases, and solids in demanding environments. Their controlled manufacturing process, tight dimensional tolerances, and guaranteed minimum wall thickness make them the preferred choice over seamless pipes for large-diameter, heavy-wall, and safety-critical applications (offshore, nuclear, high-temperature steam lines). For standard sizes and large production lots, seamless pipes remain more economical.
Leave a Comment
Have a question or feedback? Send us a message.
Previous Comments
Nice Information
I think that this article is really very informative. You have explained the various applications of Stainless Steel Seamless Pipes and forged pipes in this article. You have also explained the materials and sizes in great detail. I have clearly understood the difference between these two types of pipes. Thank you very much for sharing this article with us.
Interesting, could you please add the names of the suppliers of forged pipes in Europe? We have been scouting for suppliers lately, without success. help appreciated, Mark
Dear Mark, please get in touch with us. We will send you the list of the forged steel pipes manufacturers in Italy (among the top world's suppliers, both in terms of technical know how and cost effectiveness) and in Germany. Thank you for your interest in our article. Best, Projectmaterials
Very detailed information providing specific details of each type of pipe. Thanks for Sharing
Nice info, Goyal Steel Tubes, the oldest dealer of MS Pipes and Tubes in Delhi-NCR, deals in all sizes and variety of MS Pipes, stocked from reputed companies like APL Apollo, Jindal, Surya etc. Send your pipe related queries on 9650705448, call on 9910495448 or find us on google- Goyal Steel Tubes click on the first link.
Hi, Adorable Blog and this is something new I am reading on Blogger, we are Sandco Metal Industries We are leading,stainless steel pipe manufacturers in ahmedabad,stainless steel pipe manufacturers in delhi,stainless steel pipe manufacturer in India,Stainless Steel Pipe Weight Chart,Stainless Steel Pipe Manufacturer in Saudi Arabia and Stainless Steel Pipe Manufacturer in Bhubaneswar</a
Hi, Adorable Blog and this is something new I am reading on Blogger, we are DChel Weld We are leading,welding electrodes manufacturer in India, Welding electrodes manufacturer in Gujarat, Welding Electrode Manufacturer in Bangladesh, Welding Electrode Manufacturer in Bangalore
Well written blog, we are certified Stainless Steel Pipe Manufacturer, Supplier in Kenya
Hello, Very Informative article. It was nice to read the information you shared in the blog. Also if you are looking for Stainless Steel Round Bar Manufacturer in India do visit Girish Metal India.
Thank you for your appreciation and for sharing the link to Metalica Forging Inc. It's great to see that you are a market leader in the field of stainless steel flange manufacturing in India. Your expertise in this area must be valuable to those seeking high-quality flanges. In the context of the previous conversation about forged and seamless pipes, it's interesting to note that both forged and seamless manufacturing processes are crucial in producing various components, including flanges. The article highlights the differences between forged and seamless pipes, such as the manufacturing process, sizes denominations, dimensional range, and applications. Considering your expertise in manufacturing stainless steel flanges, it would be insightful to discuss how the manufacturing processes for pipes and flanges differ, and how these differences might impact the final product. Additionally, if you have any specific insights or experiences related to the topic of forged or seamless flanges, we would greatly appreciate your input. Thank you again for sharing your knowledge and expertise on stainless steel flange manufacturing in India.
Thank you for your kind words, Girish Metal India! We're glad to hear that you found the article on forged vs. seamless pipes informative. It's always great to provide valuable information to our readers. We appreciate you sharing your link for Stainless Steel Round Bar Manufacturers in India. It's important to have reliable sources when looking for specific products. We encourage our readers to explore different options and find the best manufacturers that suit their needs. If you have any further insights or thoughts on the topic of forged vs. seamless pipes, we'd love to hear them. Thank you again for your contribution to the discussion!