Heavy Hex Nut Sizes & A194 Chart
Hex Nuts and Washers for Stud Bolts
Bolt and Nut Size Chart Overview
Nuts and washers directly affect the clamping force and service life of stud bolt connections. This is true across general construction and high-pressure, high-temperature piping systems in petrochemical plants.
 nuts and washers for stud bolts
nuts and washers for stud bolts
Nuts for Stud Bolts
Nuts thread onto the exposed ends of stud bolts and apply the clamping force that holds flanged joints together. Adjusting how far the nut is tightened controls the bolt tension. The three main types used in piping service are:
| Nut Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Hex nuts | The standard choice for most applications. Typically installed in pairs, one on each end of the stud bolt. Good balance of size, bearing area, and wrenchability. |
| Heavy hex nuts | Larger and thicker than standard hex nuts. The wider bearing face spreads load over a greater area, which matters in high-pressure flanged connections. These are the default nut for ASME B16.5 flanges. |
| Lock nuts | Resist loosening under vibration and cyclic loading. Variants include nylon-insert (nyloc) nuts and distorted-thread types. |
Washers for Stud Bolts
Washers spread the load from the nut across a wider area, preventing the nut from gouging or galling the flange face. They also protect finished surfaces during tightening and help maintain preload as the joint cycles through thermal expansion and contraction.
| Washer Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Flat washers | The most basic type. They increase bearing area and protect the contact surface from damage. |
| Spring washers (Belleville) | Conical disc washers that act as springs, maintaining bolt tension in services subject to vibration or thermal cycling. |
| Lock washers | Split-ring (helical) or toothed designs that grip the nut and mounting surface to resist back-off. |
Application Considerations
Selecting the right nut and washer combination depends on the mechanical load, operating temperature, corrosive environment, and vibration exposure of the joint. Carbon steel hardware suits most general-purpose service; stainless steel and specialty alloys are required where corrosion resistance or elevated temperature strength matters.
Key Takeaway: In high-stress or critical applications, such as flanged connections in the oil and gas industry, correct selection and installation of nuts, washers, and stud bolts directly governs joint integrity and safety. Routine inspection and maintenance extend service life and prevent in-service failures.
Dimensional Charts
The chart below shows the hex nuts’ width and thicknesses by diameter:
 Heavy Hex Nuts Dimensions ASME B18.2.2
Heavy Hex Nuts Dimensions ASME B18.2.2
| Diameter (inches) | F Basic | F Max | F Min | C Max | C Min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2 | 7/8 | 0.875 | 0.850 | 1.010 | 0.969 |
| 5/8 | 1.1/16 | 1.062 | 1.031 | 1.227 | 1.175 |
| 3/4 | 1.1/4 | 1.250 | 1.212 | 1.443 | 1.382 |
| 7/8 | 1.7/16 | 1.438 | 1.394 | 1.660 | 1.589 |
| 1 | 1.5/8 | 1.625 | 1.575 | 1.876 | 1.796 |
| 1⅛ | 1.13/16 | 1.812 | 1.756 | 2.093 | 2.002 |
| 1¼ | 2 | 2.000 | 1.938 | 2.309 | 2.209 |
| 1⅜ | 2.3/16 | 2.188 | 2.119 | 2.526 | 2.416 |
| 1½ | 2.3/8 | 2.375 | 2.300 | 2.742 | 2.622 |
| 1⅝ | 2.9/16 | 2.562 | 2.481 | 2.959 | 2.828 |
| 1¾ | 2.3/4 | 2.750 | 2.662 | 3.175 | 3.035 |
| 1⅞ | 2.15/16 | 2.938 | 2.844 | 3.392 | 3.242 |
| 2 | 3.1/8 | 3.125 | 3.025 | 3.608 | 3.449 |
| 2¼ | 3.1/2 | 3.500 | 3.388 | 4.041 | 3.862 |
| 2½ | 3.7/8 | 3.875 | 3.750 | 4.474 | 4.275 |
| 2¾ | 4.1/4 | 4.250 | 4.112 | 4.907 | 4.688 |
| 3 | 4.5/8 | 4.625 | 4.475 | 5.340 | 5.102 |
| 3¼ | 5 | 5.000 | 4.838 | 5.774 | 5.515 |
| 3½ | 5.3/8 | 5.375 | 5.200 | 6.207 | 5.928 |
| 3¾ | 5.3/4 | 5.750 | 5.562 | 6.640 | 6.341 |
| 4 | 6.1/8 | 6.125 | 5.925 | 7.073 | 6.755 |
 Heavy Hex Nuts Dimensions ASME B18.2.2
Heavy Hex Nuts Dimensions ASME B18.2.2
| Diameter (inches) | Thickness Basic | Thickness Max | Thickness Min |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2 | 31/64 | 0.504 | 0.464 |
| 5/8 | 39/64 | 0.631 | 0.587 |
| 3/4 | 47/64 | 0.758 | 0.710 |
| 7/8 | 55/64 | 0.885 | 0.833 |
| 1 | 63/64 | 1.012 | 0.956 |
| 1⅛ | 1.7/64 | 1.139 | 1.079 |
| 1¼ | 1.7/32 | 1.251 | 1.187 |
| 1⅜ | 1.11/32 | 1.378 | 1.310 |
| 1½ | 1.15/32 | 1.505 | 1.433 |
| 1⅝ | 1.19/32 | 1.632 | 1.556 |
| 1¾ | 1.23/32 | 1.759 | 1.679 |
| 1⅞ | 1.27/32 | 1.886 | 1.802 |
| 2 | 1.31/32 | 2.013 | 1.925 |
| 2¼ | 2.13/64 | 2.251 | 2.155 |
| 2½ | 2.29/64 | 2.505 | 2.401 |
| 2¾ | 2.45/64 | 2.759 | 2.647 |
| 3 | 2.61/64 | 3.013 | 2.893 |
| 3¼ | 3.3/16 | 3.252 | 3.124 |
| 3½ | 3.7/16 | 3.506 | 3.370 |
| 3¾ | 3.11/16 | 3.760 | 3.616 |
| 4 | 3.15/16 | 4.014 | 3.862 |
Weights
Hex Nuts Weight in Lbs
Hex nuts weight in Lbs (pounds/ 100 pieces) by diameter:
| Heavy Hex Nuts Diameter | Finished Hex | Heavy Hex | Finished Jam | Heavy Hex Jam | Square | Heavy Square |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2″ | 3.75 | 6.54 | 2.62 | 4 | 5.78 | 7.87 |
| 5/8″ | 7.33 | 11.9 | 4.93 | 6.96 | 10.8 | 14.3 |
| 3/4″ | 11.9 | 19.3 | 7.7 | 11 | 15.4 | 23.5 |
| 7/8″ | 19 | 29.7 | 12 | 16.7 | 24.5 | 36.2 |
| 1″ | 28.3 | 42.5 | 17.6 | 23.5 | 36.3 | 51.5 |
| 1-1/8″ | 40.3 | 59.2 | 24.7 | 32.4 | 52.5 | 72.4 |
| 1-1/4″ | 54.3 | 78.6 | 36.1 | 45.8 | 70.6 | 95.5 |
| 1-3/8″ | 73 | 102 | 47.9 | 59.3 | 94.5 | 125 |
| 1-1/2″ | 94.3 | 131 | 60.9 | 74.8 | 122 | 161 |
| 1-5/8″ | 162 | 91.6 | ||||
| 1-3/4″ | 151 | 204 | 100 | 114 | ||
| 1-7/8″ | 241 | 134 | ||||
| 2″ | 224 | 299 | 140 | 165 | ||
| 2-1/4″ | 419 | 227 | ||||
| 2-1/2″ | 564 | 332 | ||||
| 2-3/4″ | 738 | 429 | ||||
| 3″ | 950 | 545 | ||||
| 3-1/4″ | 1194 | 651 | ||||
| 3-1/2″ | 1526 | 851 | ||||
| 3-3/4″ | 1812 | 1005 | ||||
| 4″ | 2180 | 1200 |
The weight of heavy hexagonal steel nuts for stud bolts in lbs / 100 units - ASME B18.2.2
Hex Nuts Weight in Kilograms
Hex nuts weight in Kgs. (kg/100 pieces) by diameter:
| Heavy Hex Nuts Diameter | Finished Hex | Heavy Hex | Finished Jam | Heavy Hex Jam | Square | Heavy Square |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2″ | 1.70 | 2.97 | 1.19 | 1.81 | 2.62 | 3.57 |
| 5/8″ | 3.32 | 5.40 | 2.24 | 3.16 | 4.90 | 6.49 |
| 3/4″ | 5.40 | 8.75 | 3.49 | 4.99 | 6.98 | 10.66 |
| 7/8″ | 8.62 | 13.47 | 5.44 | 7.57 | 11.11 | 16.42 |
| 1″ | 12.83 | 19.27 | 7.98 | 10.66 | 16.46 | 23.36 |
| 1-1/8″ | 18.28 | 26.85 | 11.20 | 14.69 | 23.81 | 32.83 |
| 1-1/4″ | 24.63 | 35.65 | 16.37 | 20.77 | 32.02 | 43.31 |
| 1-3/8″ | 33.11 | 46.26 | 21.72 | 26.89 | 42.86 | 56.69 |
| 1-1/2″ | 42.77 | 59.41 | 27.62 | 33.92 | 55.33 | 73.01 |
| 1-5/8″ | 0.00 | 73.47 | 0.00 | 41.54 | ||
| 1-3/4″ | 68.48 | 92.51 | 45.35 | 51.70 | ||
| 1-7/8″ | 0.00 | 109.29 | 0.00 | 60.77 | 0.00 | |
| 2″ | 101.58 | 135.60 | 63.49 | 74.83 | 0.00 | |
| 2-1/4″ | 190.02 | 0.00 | 102.94 | 0.00 | ||
| 2-1/2″ | 255.77 | 0.00 | 150.56 | 0.00 | ||
| 2-3/4″ | 334.68 | 0.00 | 194.55 | 0.00 | ||
| 3″ | 430.83 | 0.00 | 247.16 | 0.00 | ||
| 3-1/4″ | 541.48 | 0.00 | 295.23 | 0.00 | ||
| 3-1/2″ | 692.04 | 0.00 | 385.93 | 0.00 | ||
| 3-3/4″ | 821.74 | 0.00 | 455.77 | 0.00 | ||
| 4″ | 988.63 | 0.00 | 544.20 |
The weight of heavy hexagonal steel nuts for stud bolts in kilograms / 100 units - ASME B18.2.2
Stud Bolt Weight in Kgs (Stud + 2 Hex Nuts)
Complete stud bolt assembly weight in Kgs. (kg/100 pieces) by metric size:
| Heavy Hex Nuts Diameter (Metric) | Bolt Weight (kg) | Nut Weight (kg) | Total Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M12 x 35 | 0.049 | 0.013 | 0.062 |
| M12 x 40 | 0.053 | 0.013 | 0.066 |
| M12 x 45 | 0.058 | 0.013 | 0.071 |
| M12 x 50 | 0.062 | 0.013 | 0.075 |
| M12 x 55 | 0.067 | 0.013 | 0.080 |
| M12 x 60 | 0.071 | 0.013 | 0.084 |
| M12 x 65 | 0.072 | 0.013 | 0.085 |
| M12 x 70 | 0.080 | 0.013 | 0.093 |
| M12 x 75 | 0.085 | 0.013 | 0.098 |
| M12 x 80 | 0.089 | 0.013 | 0.102 |
| M12 x 85 | 0.094 | 0.013 | 0.107 |
| M12 x 90 | 0.098 | 0.013 | 0.111 |
| M12 x 95 | 0.103 | 0.013 | 0.116 |
| M12 x 100 | 0.107 | 0.013 | 0.120 |
| M12 x 105 | 0.111 | 0.013 | 0.124 |
| M12 x 110 | 0.116 | 0.013 | 0.129 |
| M 16X35 | 0.087 | 0.032 | 0.119 |
| M 16X40 | 0.094 | 0.032 | 0.126 |
| M 16X45 | 0.102 | 0.032 | 0.134 |
| M 16X50 | 0.110 | 0.032 | 0.142 |
| M 16X55 | 0.118 | 0.032 | 0.150 |
| M 16X60 | 0.126 | 0.032 | 0.158 |
| M 16X65 | 0.132 | 0.032 | 0.164 |
| M 16X70 | 0.141 | 0.032 | 0.173 |
| M 16X75 | 0.148 | 0.032 | 0.180 |
| M 16X80 | 0.153 | 0.032 | 0.185 |
| M 16X85 | 0.161 | 0.032 | 0.193 |
| M 16X90 | 0.167 | 0.032 | 0.199 |
| M 16X95 | 0.177 | 0.032 | 0.209 |
| M 16X100 | 0.186 | 0.032 | 0.218 |
| M 16X105 | 0.195 | 0.032 | 0.227 |
| M 16X110 | 0.203 | 0.032 | 0.235 |
| M 16X115 | 0.211 | 0.032 | 0.243 |
| M 16X120 | 0.220 | 0.032 | 0.252 |
| M 16X125 | 0.228 | 0.032 | 0.260 |
| M 16X130 | 0.235 | 0.032 | 0.267 |
| M 16X135 | 0.243 | 0.032 | 0.275 |
| M 16X140 | 0.251 | 0.032 | 0.283 |
| M 16X145 | 0.259 | 0.032 | 0.291 |
| M 16X150 | 0.267 | 0.032 | 0.299 |
| M 16X155 | 0.270 | 0.032 | 0.302 |
| M 16X160 | 0.278 | 0.032 | 0.310 |
| M 16X165 | 0.286 | 0.032 | 0.318 |
| M 16X170 | 0.294 | 0.032 | 0.326 |
| M 16X175 | 0.302 | 0.032 | 0.334 |
| M 16X180 | 0.310 | 0.032 | 0.342 |
| M 16X185 | 0.318 | 0.032 | 0.350 |
| M 16X190 | 0.326 | 0.032 | 0.358 |
| M 16X195 | 0.334 | 0.032 | 0.366 |
| M 16X200 | 0.342 | 0.032 | 0.374 |
| M 20X45 | 0.173 | 0.061 | 0.234 |
| M 20X50 | 0.186 | 0.061 | 0.247 |
| M 20X55 | 0.198 | 0.061 | 0.259 |
| M 20X60 | 0.211 | 0.061 | 0.272 |
| M 20X65 | 0.223 | 0.061 | 0.284 |
| M 20X70 | 0.235 | 0.061 | 0.296 |
| M 20X75 | 0.248 | 0.061 | 0.309 |
| M 20X80 | 0.260 | 0.061 | 0.321 |
| M 20X85 | 0.273 | 0.061 | 0.334 |
| M 20X90 | 0.285 | 0.061 | 0.346 |
| M 20X95 | 0.297 | 0.061 | 0.358 |
| M 20X100 | 0.310 | 0.061 | 0.371 |
| M 20X105 | 0.322 | 0.061 | 0.383 |
| M 20X110 | 0.334 | 0.061 | 0.395 |
| M 20X115 | 0.346 | 0.061 | 0.407 |
| M 20X120 | 0.359 | 0.061 | 0.420 |
| M 20X125 | 0.371 | 0.061 | 0.432 |
| M 20X130 | 0.384 | 0.061 | 0.445 |
| M 20X135 | 0.396 | 0.061 | 0.457 |
| M 20X140 | 0.408 | 0.061 | 0.469 |
| M 20X145 | 0.421 | 0.061 | 0.482 |
| M 20X150 | 0.433 | 0.061 | 0.494 |
| M 20X155 | 0.445 | 0.061 | 0.506 |
| M 20X160 | 0.458 | 0.061 | 0.519 |
| M 20X165 | 0.470 | 0.061 | 0.531 |
| M 20X170 | 0.482 | 0.061 | 0.543 |
| M 20X175 | 0.495 | 0.061 | 0.556 |
| M 20X180 | 0.506 | 0.061 | 0.445 |
| M 20X185 | 0.518 | 0.061 | 0.457 |
| M 20X190 | 0.530 | 0.061 | 0.469 |
| M 20X195 | 0.542 | 0.061 | 0.481 |
| M 20X200 | 0.554 | 0.061 | 0.493 |
| M 24X45 | 0.258 | 0.104 | 0.362 |
| M 24X50 | 0.276 | 0.104 | 0.380 |
| M 24X55 | 0.294 | 0.104 | 0.398 |
| M 24X60 | 0.312 | 0.104 | 0.416 |
| M 24X65 | 0.330 | 0.104 | 0.434 |
| M 24X70 | 0.348 | 0.104 | 0.452 |
| M 24X75 | 0.366 | 0.104 | 0.470 |
| M 24X80 | 0.384 | 0.104 | 0.488 |
| M 24X85 | 0.402 | 0.104 | 0.506 |
| M 24X90 | 0.420 | 0.104 | 0.524 |
| M 24X95 | 0.437 | 0.104 | 0.541 |
| M 24X100 | 0.456 | 0.104 | 0.560 |
| M 24X105 | 0.471 | 0.104 | 0.575 |
| M 24X110 | 0.492 | 0.104 | 0.596 |
| M 24X115 | 0.510 | 0.104 | 0.614 |
| M 24X120 | 0.528 | 0.104 | 0.632 |
| M 24X125 | 0.546 | 0.104 | 0.650 |
| M 24X130 | 0.559 | 0.104 | 0.663 |
| M 24X135 | 0.582 | 0.104 | 0.686 |
| M 24X140 | 0.598 | 0.104 | 0.702 |
| M 24X145 | 0.618 | 0.104 | 0.722 |
| M 24X150 | 0.638 | 0.104 | 0.742 |
| M 24X155 | 0.656 | 0.104 | 0.760 |
| M 24X160 | 0.674 | 0.104 | 0.778 |
| M 24X165 | 0.688 | 0.104 | 0.792 |
| M 24X170 | 0.709 | 0.104 | 0.813 |
| M 24X175 | 0.727 | 0.104 | 0.831 |
| M 24X180 | 0.745 | 0.104 | 0.849 |
| M 24X185 | 0.762 | 0.104 | 0.866 |
| M 24X190 | 0.78 | 0.104 | 0.884 |
| M 24X195 | 0.798 | 0.104 | 0.902 |
| M 24X200 | 0.816 | 0.104 | 0.920 |
Hex Nuts Materials
ASTM A194 Material Specification
The ASTM A194 specification covers carbon, alloy, martensitic, and austenitic stainless steel nuts. Hex-heavy nuts are components of boltings sets for flanges. These nuts are intended for high-pressure or high-temperature service or both, and the bars from which they are made must be hot-wrought.
Per ASTM A194, the material may be further processed by centerless grinding or cold drawing. Austenitic stainless steel may be solution annealed or annealed and strain-hardened. Each alloy must conform to its prescribed chemical composition requirements. Hardness tests, proof-of-load tests, and cone-proof-load tests are mandatory for all nuts.
Key ASTM A194 Parameters
| Parameter | Detail |
|---|---|
| Size range | 1/4” through 4” (metric: M6 to M100) |
| Unit systems | Inch-pound or SI (not interchangeable) |
| Threading standard | ANSI B 18.2.2 Heavy Hex Series |
| Thread fit (<=1”) | UNC Series Class 2B |
| Thread fit (>1”) | UNC Series Class 2B or 8 UN Series Class 2B |
| Most common grade | A194 2H (paired with A193 B7 studs) |
The most common grades of ASTM A194 heavy hex steel nuts are:
| Grade | Material Description |
|---|---|
| A194 2H | Quenched & tempered carbon steel |
| A194 2HM | Quenched & tempered carbon steel (controlled hardness) |
| A194 3 | Chrome-moly alloy steel |
| A194 4 | Quenched & tempered carbon-molybdenum |
| A194 6 | Martensitic stainless steel |
| A194 7 | Quenched & tempered alloy steel (AISI 4140) |
| A194 7M | Quenched & tempered alloy steel (controlled hardness) |
| A194 8 | Stainless AISI 304 |
| A194 8A | Stainless AISI 304 (solution annealed) |
| A194 8M | Stainless AISI 316 |
| A194 8MA | Stainless AISI 316 (solution annealed) |
| A194 8C | Stainless AISI 347 (stabilized) |
| A194 8T | Stainless AISI 321 (stabilized) |
ASTM A194 Chemical Composition
| ASTM A194 NUTS | Carbon | Manganese | Phosphorous, max | Sulfur, max | Silicon | Chromium | Nickel | Molybdenum | Other Elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM A194 grade 2, 2H and 2 HM | 0.40% min. | 1.00% max. | 0.04% | 0.05% | 0.40% max | ||||
| ASTM A194 grade 3 | 0.10% min. | 1.00% max. | 0.04% | 0.03% | 1.00% | 4.0-6.0% | 0.20-0.30% | ||
| ASTM A194 grade 4 | 0.40 -0.50% | 0.70-0.90% | 0.035% | 0.04% | 0.15-0.35% | 0.20-0.30% | |||
| ASTM A194 grade 6 | 0.15% | 1.00% | 0.04% | 0.03% | 1.00% | 11.5-13.5% | |||
| ASTM A194 grade 6F | 0.15% | 1.25% | 0.06% | 0.06% | 1.00% | 12.0-14.0% | Selenium-0.15% min | ||
| ASTM A194 grade 7 and 7M (AISI 4140) | 0.37-0.49% | 0.65-1.10% | 0.04% | 0.04% | 0.15-0.035% | 0.75-1.20% | 0.15-0.25% | ||
| ASTM A194 grade 8 (AISI 304) | 0.08% | 2.00% max | 0.05% | 0.03% | 1.00% max | 18.0-20.0% | 8.0-11.0% | ||
| ASTM A194 grade 8M (AISI 316) | 0.08% | 2.00% max | 0.05% | 0.30% | 1.00% max | 16.0-18.0% | 10.0-14.0% | 2.00-3.00% | |
| ASTM A194 grade 8C | 0.08% | 2.00% | 0.045% | 0.03% | 1.00% | 17.0-19.0% | 9.0-12.0% | Columbium and Tantalum - 10x carbon content, min | |
| ASTM A194 grade 8T | 0.80% | 2.00% | 0.045% | 0.30% | 1.00% | 17.0-19.0% | 9.0-12.0% | Titanium-0.70%max, Nitrogen-0.10% | |
| ASTM A194 grade 8F | 0.15% | 2.00% | 0.20% | 0.15%min | 1.00% | 17.0-19.0% | 8.0-10.0% | ||
| ASTM A194 grade 8R | 0.06% | 4.0-6.0% | 0.045% | 0.03% | 1.00% | 20.5-23.5% | 11.5-13.5% | 1.50-3.00% | Columbium and Tantalum-0.10-0.30%, Nirogen-0.20-0.40%, Vanadium-0.10-0.30% |
| ASTM A194 grade 8S | 0.10% | 7.0-9.0% | 0.060% | 0.03% | 3.5-4.5% | 16.0-18.0% | 8.0-9.0% | Nitrogen-0.08-0.18% | |
| ASTM A194 grade 16 | 0.36-0.47% | 0.45-0.70% | 0.035% | 0.40% | 0.15-0.35% | 0.80-1.15% | 0.50-0.65% |
ASTM A194 Mechanical Properties
| Grade Marking | Specification | Material | Nominal Size (In.) | Tempering Temp (°F) | Proof Load Stress (ksi) | Hardness Min | Hardness Max | See Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
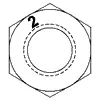 | ASTM A194 Grade 2 | Medium Carbon Steel | 1/4 - 4 | 0 | 150 | 159 | 352 | 1,2,3 |
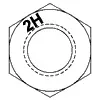 | ASTM A194 Grade 2H | Medium Carbon Steel, Quenched and Tempered | 1/4 - 4 | 850 | 175 | C24 | C38 | 1,2 |
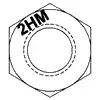 | ASTM A194 Grade 2HM | Medium Carbon Steel, Quenched and Tempered | 1/4 - 4 | 1150 | 150 | 159 | 237 | 1,2,3 |
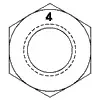 | ASTM A194 Grade 4 | Medium Carbon Alloy Steel, Quenched and Tempered | 1/4 - 4 | 1100 | 175 | C24 | C38 | 1,2 |
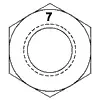 | ASTM A194 Grade 7 | Medium Carbon Alloy Steel, Quenched and Tempered | 1/4 - 4 | 1100 | 175 | C24 | C38 | 1,2 |
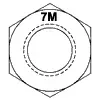 | ASTM A194 Grade 7M | Medium Carbon Alloy Steel, Quenched and Tempered | 1/4 - 4 | 1150 | 150 | 159 | 237 | 1,2,3 |
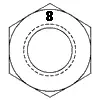 | ASTM A194 Grade 8 | Stainless AISI 304 | 1/4 - 4 | - | 80 | 126 | 300 | 4 |
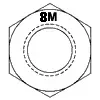 | ASTM A194 Grade 8M | Stainless AISI 316 | 1/4 - 4 | - | 80 | 126 | 300 | 4 |
Other ASTM Grades for Hex Nuts
Beyond A194, several other ASTM specifications cover hex nuts for different materials and service conditions.
ASTM A563
This specification covers carbon and alloy steel nuts for general structural and mechanical use. Grades range from Grade A (mild carbon steel) through Grade C (medium carbon, quenched and tempered) to Grade DH (carbon steel, quenched and tempered for high-strength bolting).
ASTM F594
Covers stainless steel nuts for general engineering applications. Nuts are classified by alloy group (304, 316, 321) with condition designators indicating strength level: CW for cold worked, A for annealed.
ASTM F467
Covers nonferrous nuts made from aluminum, copper, and nickel alloys for general use. Grades are categorized by base material and temper, for example Aluminum Alloy 6061-T6.
ASTM A563M (Metric)
The metric counterpart to ASTM A563, covering carbon and alloy steel nuts in metric sizes. Grades and property classes parallel those of A563 but use metric dimensions and SI strength units.
ASTM F836M
The metric version of ASTM F594, specifying stainless steel nuts in metric sizes for general engineering use. Classified by alloy group and condition, following the same framework as F594 but with metric measurements.
European Material Grades Specs for Nuts
European standards for hex nuts used in flanged connections serve the industrial, construction, and energy sectors. The key specifications are summarized below.
EN ISO 4032
Covers style-1 hexagonal nuts in threads from M1.6 through M64. Product grade A applies to threads up to M16; product grade B applies above M16. These are the general-purpose nuts used across most flanged connections.
EN ISO 4033
Similar scope to EN ISO 4032 but specifies hexagonal high nuts (taller profile). Used where longer thread engagement is needed or where the assembly calls for a thicker nut body.
EN ISO 4034
Covers style-1 hexagonal nuts in threads from M5 through M39, product grade C. Intended for less critical applications where coarser dimensional tolerances are acceptable.
EN ISO 4035
Covers hexagon thin nuts (chamfered) with metric fine-pitch thread, product grades A and B. Used where axial space is limited, including certain flange connections.
EN ISO 4036
Covers hexagon thin nuts (unchamfered) with metric fine-pitch thread, product grades A and B. Similar application range to EN ISO 4035, for thin-nut service without a chamfer.
EN 1092-1
Primarily a flange standard, but EN 1092-1 indirectly sets requirements for bolts and nuts in flanged connections by specifying flange types, dimensions, and materials for various pressure-temperature combinations.
Common ISO Grades for Nuts
Steel nuts in Europe follow ISO classification, which provides a uniform framework for mechanical properties across international borders.
ISO 898-2 for Carbon Steel and Alloy Steel Nuts
ISO 898-2 groups nuts into property classes based on proof load capacity:
| Property Class | Strength Level | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Class 6 | Low strength | Light-duty assemblies where high tensile load is not a factor |
| Class 8 | Medium strength | General engineering and structural applications |
| Class 10 | High strength | Applications requiring good tensile strength and hardness |
| Class 12 | Very high strength | Demanding structural and mechanical joints |
ISO 3506-2 for Stainless Steel Nuts
The two primary stainless grades are A2 and A4:
| Grade | Equivalent | Corrosion Resistance | Typical Service |
|---|---|---|---|
| A2 | AISI 304 | Good in standard atmospheric and mild chemical environments | Indoor and outdoor general-purpose applications |
| A4 | AISI 316 | Superior, especially in chloride and marine exposure, due to molybdenum content | Marine, offshore, and chemical process environments |
Tensile/Yield Strength Classification (8.8/10.9 Nuts)
The ISO 898 grading system uses a two-number code to describe mechanical properties of hex nuts:
- The first number multiplied by 100 gives the approximate minimum ultimate tensile strength in MPa.
- The second number, multiplied by the first, gives the ratio of yield strength to tensile strength.
8.8 Grade nuts have a minimum tensile strength of 800 MPa and a yield strength of approximately 640 MPa (0.8 x 800). They are made from medium carbon steel or alloy steel and can be heat-treated. Zinc or other protective coatings are common. Grade 8.8 sees wide use in automotive, construction, and manufacturing assemblies that require moderate strength and toughness.
10.9 Grade nuts have a minimum tensile strength of 1000 MPa and a yield strength of approximately 900 MPa (0.9 x 1000). These are typically alloy steel, heat-treated to reach the higher strength range. Like 8.8 hardware, they accept corrosion-resistant coatings. Grade 10.9 is specified for heavy machinery, structural steelwork, and any joint under high static or dynamic loading.
Selection Factors
When choosing a hex nut grade, three factors drive the decision. First, the mechanical loading and environmental conditions of the joint (temperature extremes, cyclic stress, vibration) determine the minimum property class. Second, corrosion resistance requirements dictate whether carbon steel, A2 stainless, or A4 stainless is needed; A4 is the standard choice for marine and chemical-plant service. Third, the required proof load and hardness range must match the stud bolt grade to avoid galling or under-clamping the joint.
Leave a Comment
Have a question or feedback? Send us a message.
Previous Comments
You can find an answer by looking at the chemical and mechanical tables posted on our blog. thanks.
is there any codes (ASME, ASTM, etc.) recommend pairing of bolt and nut type (i.e B7 bolt & 2H nut)