CE Marking for Steel Products: Compliance
CE Marking for Steel Products
What Is “CE Marking”?
The CE marking, standing for “Conformité Européenne” (European Conformity), is a mandatory conformity mark for products within the European Economic Area (EEA). It signifies that the product meets high safety, health, and environmental protection requirements.
For steel products, the CE mark is a declaration from the manufacturer that these products comply with the relevant European product standards and performance characteristics.

The term initially used was “EC Mark” but this terminology was officially replaced by “CE Marking” after the issuance of Directive 93/68/EEC in 1993.
Relevance of “CE Marking”
The construction industry relies heavily on steel products, and safety and reliability in this sector cannot be compromised. Steel beams, columns, reinforcements, and other structural elements are fundamental to the stability and longevity of buildings and infrastructure.
The CE marking on these steel products confirms adherence to European Union standards for safety, durability, and quality, which are among the strictest in the world.
Beyond structural applications, other steel products (including steel pipes) must be CE marked to be legally distributed and installed within EU member states. This requirement is particularly important for imported steel products (for example, those of Chinese and Indian origin) as non-CE marked products may be considered illegal and subject to sanctions for the manufacturer/distributor and the end-user alike.
Benefits of CE Marking for Steel Products
CE marking on steel products delivers tangible advantages to manufacturers, specifiers, and end-users.
| Benefit | What It Means in Practice |
|---|---|
| Access to the European Market | Products bearing the CE mark can be freely traded within the EEA, removing trade barriers across member states. |
| Quality Assurance | Engineers, architects, and contractors gain documented proof that the steel products they specify meet the highest European safety and quality standards. |
| Competitive Advantage | Manufacturers with CE marking demonstrate to buyers that their products satisfy stringent EU regulations, differentiating them in the market. |
| Risk Reduction | CE-marked steel products have undergone rigorous testing and performance assessment, lowering the risk of structural failures and the associated liabilities. |
How to Achieve CE Marking
To achieve CE marking, steel products must undergo evaluations and tests confirming they meet the technical standards set out by the European Union. The process covers the following areas:
| Step | Details |
|---|---|
| Factory Production Control (FPC) | Manufacturers must implement and maintain an FPC system, assessed by a notified body, to demonstrate consistent manufacturing quality and product conformity. |
| Product Testing | Depending on the applicable harmonized European standards, steel products undergo tests for mechanical properties, chemical composition, and dimensional accuracy. |
| Technical Documentation | Manufacturers compile evidence of conformity: test results, product descriptions, technical drawings, and calculations. |
| Declaration of Performance (DoP) | After assessment, the manufacturer drafts a DoP detailing the product’s essential characteristics and performance per EU standards. |
| Affixing the CE Mark | The manufacturer applies the CE mark to products, packaging, or accompanying documents. The mark must be visible, legible, and indelible. |
The manufacturer must also follow administrative steps depending on the product type and associated risk:
- Determine which directives apply to the product. If more than one applies, the manufacturer must comply with all of them.
- Determine the extent to which the product meets the essential requirements for design and manufacturing in the applicable directive(s).
- Choose the conformity assessment procedure from the options specified by the directive. The available modules for Conformity Assessment Procedures are listed below:
| Module | Description |
|---|---|
| Module A | Internal production control |
| Module Aa | Intervention of a Notified Body |
| Module B | EC type-examination |
| Module C | Conformity to type |
| Module D | Production Quality Assurance |
| Module E | Product Quality Assurance |
| Module F | Product verification |
| Module G | Unit verification |
| Module H | Full quality assurance |
The directives often use a series of questions about the nature of the product to classify the level of risk and refer to a chart called “Conformity Assessment Procedures.”
The chart includes all acceptable options available to a manufacturer to certify their product and affix the CE Marking.
Self or Third-Party CE Certification?
Low-Risk Products (Autocertification)
Auto-certification is a simplified CE marking procedure where the manufacturer declares that their product meets EU regulatory requirements without an independent third-party assessment by a notified body. This path applies under specific conditions for product categories where the risk to health, safety, and environment is considered lower.
Criteria for Auto-certification
Three factors determine whether auto-certification is permissible:
| Factor | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Product Category and Risk Profile | The product must fall under directives or regulations classified as lower risk. EU legislation identifies which categories qualify and under what conditions a manufacturer can self-declare conformity. |
| Harmonized Standards | The product must comply with the relevant harmonized European standards, which provide the technical specifications and guidelines for health, safety, and environmental protection requirements. |
| Conformity Assessment Procedures | The governing directive or regulation must allow assessment without a notified body, permitting the manufacturer to conduct necessary tests and assessments in-house. |
Steps for Auto-certification
The auto-certification process follows four stages:
-
Internal Production Control: The manufacturer must operate a thorough internal production control system to verify that all manufactured products consistently meet EU standards and regulations.
-
Technical Documentation: The manufacturer compiles and maintains detailed documentation covering the design, manufacture, and operation of the product, demonstrating how it satisfies the relevant requirements.
-
EU Declaration of Conformity (DoC): The manufacturer drafts a DoC, a legal document formally declaring that the product complies with all applicable EU requirements. The DoC must include the manufacturer’s details, product description, and the specific directives and standards addressed.
-
Affixing the CE Mark: After completing the DoC, the manufacturer applies the CE mark to the product, packaging, or accompanying documentation. The mark must be visible, legible, and permanent.
Products Typically Eligible for Auto-certification
- Simple Pressure Vessels: Subject to specific conditions under the Simple Pressure Vessels Directive.
- Certain Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Lower-risk PPE categories may qualify for self-certification, depending on the specifics of the PPE Regulation.
- Non-critical products: Any device, tool, or assembly that does not threaten health and safety. Note that most structural pipes, sheets, plates, and other steel fall into the “critical” category and require third-party assessment instead.
Benefits and Responsibilities
Auto-certification streamlines market entry by reducing the time and cost of third-party assessments. However, it places full responsibility for compliance squarely on the manufacturer. Non-compliance can lead to penalties, including product recalls and bans from the EU market. Manufacturers opting for this route must rigorously adhere to all relevant standards and maintain proper documentation.
High-Risk Products
For products considered high-risk (and most steel products fall into this category), a Notified Body must be involved to obtain CE Marking. A Notified Body is an organization designated by EU countries to assess product conformity before the product is placed (sold or installed) on the market.
The process involves:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Identify Directives and Standards | As with self-certification, the first step is identifying which directives and standards apply to the product. |
| 2. Engage a Notified Body | The manufacturer must choose an appropriate Notified Body to assess product conformity. The choice can depend on the product type and the services the body is accredited to perform. |
| 3. Product Testing and Assessment | The Notified Body conducts or oversees the testing and assessment of the product to verify it meets the EU requirements. This may involve examining the technical design, manufacturing process, and performing specific tests. |
| 4. Technical Documentation Review | The Notified Body reviews the technical documentation prepared by the manufacturer to confirm it meets compliance requirements. |
| 5. Issuance of a CE Certificate | Upon successful assessment, the Notified Body issues a certificate of conformity, allowing the manufacturer to draft the Declaration of Conformity and affix the CE mark to their product. |
Products requiring Notified Body Assessment often include those where failure could pose a significant risk to human health and safety.
A “Notified Body” is an organization nominated by a Member Government of the European Union and notified by the European Commission. Notified bodies serve as independent test labs and perform the steps called out by the applicable directives. They must hold the necessary qualifications to meet the testing requirements outlined in the directives.
Notified bodies may be private sector organizations or government agencies.
Manufacturers may choose a notified body from any EU member state, regardless of where the goods will ultimately be sold within the EU. The lists of notified bodies responsible for different products are published by the European Commission in the Official Journal of the European Communities.
A Notified Body typically offers some or all of the following services:
- Product testing
- Type-examination certificate issue
- Technical File and design dossier evaluation
- Surveillance of product and quality system
- Identification of applicable standards
If the products need certification by a Notified Body, the following steps apply:
- Select the applicable product standards and test methods, then select a Notified Body.
- Establish an Authorized Representative in the European Union: some directives require the manufacturer to designate an EU-based representative who can produce Technical Documentation (sometimes called the Technical File) on request. The CE Marking itself does not provide product details to Surveillance Authorities.
- Prepare Technical Documentation (Technical File): the directives require that a Technical File be assembled by the manufacturer. This file holds the information verifying that testing was conducted properly and that the product complies with applicable standards.
- Prepare a Declaration of Conformity. The Declaration must contain information adequate for tracing the product back to the manufacturer or the authorized representative in the EU. It may include a list of the directives and standards the product conforms to, product identification, the manufacturer’s name, address, and signature.
- Register your product in the EU. Many products (for instance, Class I Medical Devices) must be registered in the EU and, if approved, receive a Certificate of Registration. Without this certificate, the products cannot carry the CE Marking and cannot be placed on the market.
- Affix the CE Marking to your product. There are specific rules governing the CE Marking, covering the size and location of the mark, its placement on products, packaging, and shipping documents, and limitations on who is permitted to affix it.
Low or High-Risk Product?
If there is any uncertainty about product classification or certification requirements within the EU, manufacturers or distributors must seek advice from accredited professionals before exporting steel products to the EU. Regulatory compliance with CE Marking directives protects both the seller and their EU clientele from penalties associated with non-compliance. Lack of knowledge does not serve as a valid defense, and diligence is essential, especially for suppliers outside the EU who may have limited familiarity with these regulations.
Sanctions for Missing CE Marking
When a steel product is found on the European market without the required CE marking, it constitutes non-compliance with European Union regulations. The consequences can be severe for the manufacturer, importer, or distributor involved. These sanctions uphold market integrity and hold participants accountable to the EU’s standards for safety, health, and environmental protection.
The specific nature and severity of sanctions vary depending on the member state’s legislation and the circumstances of the violation, but they generally fall into the following categories.
1. Market Withdrawal or Recall
The immediate consequence is typically withdrawal of the non-compliant product from the European market. If the product is already installed in construction or other applications, a recall may follow. This action prevents further distribution and use of potentially unsafe or non-conforming products.
2. Fines and Penalties
Manufacturers, importers, or distributors found in violation of CE marking regulations face financial sanctions. These fines can be substantial and vary from country to country within the EU. The amount depends on the severity of the infraction, the perceived risk to public safety or health, and whether the non-compliance was intentional or negligent.
3. Legal Action
When non-compliance results in serious harm or poses significant risks to health and safety, criminal charges may follow. This applies especially where there is evidence of willful deceit or negligence leading to injury or environmental damage.
4. Damage to Reputation
Beyond the immediate legal and financial consequences, companies found non-compliant with CE marking regulations can suffer lasting reputational harm. In construction and engineering, industries built on trust and reliability, association with non-compliant products can lead to lost contracts and difficulty establishing future partnerships.
5. Cease and Desist Orders
Authorities may issue cease and desist orders to companies violating CE marking regulations, effectively halting the production, import, or distribution of non-compliant steel products. This can cause significant disruptions to operations and supply chains.
6. Mandatory Compliance Measures
In some cases, authorities require companies to take specific corrective actions: additional testing, certification processes, or restructured manufacturing practices to meet EU standards.
Avoiding Non-Compliance
Given the severity of these sanctions, manufacturers, importers, and distributors of steel products intended for the European market must thoroughly understand and adhere to CE marking requirements. This includes conducting proper assessment procedures, engaging with notified bodies as necessary, and maintaining full technical documentation to demonstrate compliance.
”CE” vs. “China Export” Marks
The “CE Mark” and the “China Export” mark look remarkably similar at first glance but serve entirely different purposes and originate from different regulatory environments.
Understanding this distinction matters for manufacturers, exporters, importers, and end-users, both for regulatory compliance and to avoid confusion about product quality, safety, and intended markets.
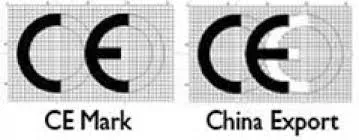
CE Mark
As discussed above, the CE Mark (Conformité Européenne / European Conformity) signifies that a product meets European Union standards for health, safety, and environmental protection. It is a mandatory conformity marking for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA), Switzerland, and Turkey. The mark indicates compliance with EU legislation and facilitates the free movement of products within the market.
Products requiring the CE Mark span a wide range: electrical equipment, machinery, medical devices, toys, and construction products, among others. The certification process involves assessing the product against the relevant EU directives and regulations, which may include safety tests, quality checks, and conformity assessments by notified bodies for certain product categories.
China Export Mark
The China Export mark is often mistakenly treated as a formal certification symbol similar to the CE Mark, but it is not an officially recognized certification mark. The confusion arises because the “China Export” mark uses a logo that closely resembles the CE Mark, with the letters “C” and “E” appearing to stand for “China Export.” In reality, no formal mark designates “China Export” in the way the CE Mark denotes European conformity. The similarity typically stems from the design of certain marks on Chinese-manufactured products that unintentionally mimic the CE logo’s appearance.
Key Differences
| Aspect | CE Mark | China Export Mark |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Regulatory mark signifying European conformity with EU safety, health, and environmental standards | No recognized or standardized meaning related to product conformity or regulatory compliance |
| Regulatory Authority | Overseen by the European Union, with strict regulations and standards that must be met for EEA market access | No governing body or formal regulations |
| Geographical Scope | Required for products entering the European market; confirms compliance with EU standards | Does not pertain to any specific regulatory requirement or geographical area |
Conclusion
Stakeholders in manufacturing, distribution, and sales of steel products must recognize the difference between the CE Mark and the commonly misunderstood China Export mark. Products intended for the European market must bear the correct CE Mark when required. Manufacturers and exporters need to be vigilant against mislabeling or confusion that could trigger regulatory issues or erode buyer trust. Knowing these distinctions helps prevent non-compliance with European safety and quality standards.
Leave a Comment
Have a question or feedback? Send us a message.
Previous Comments
WE ARE MANUFACTURE ERW M S STEEL PIPES AND HOLLOW SECTION.WE WANT BUSINESS WITH EUROPE REGION SO REQUIRED CE MARK.SO HELP US WHICH DIRECTIVE OF OUR PRODUCT? PROCESSOR SHARE STEP BY STEP
Electrical Conduit is a tube used to protect and route electrical wiring in a building or structure. Electrical Conduit may be made of metal. And plastic, fiber, or fired clay. Most conduit is rigid although but flexible conduit is used for some purposes. Newtech-pipes providing the Electric Conduit Pipes & Fittings in Pakistan. Newtech-Pipes manufactures a complete range of electrical conduit pipes and fittings. Keeping in view of quality. Call Us Now: +92333-5665265 / +92 51 4438601-4, Visit Our Website: newtech-pipes.com, Owner Name: Talha kazmi, Email: [email protected]
Electrical Conduit is a tube used to protect and route electrical wiring in a building or structure. Electrical Conduit may be made of metal. And plastic, fiber, or fired clay. Most conduit is rigid although but flexible conduit is used for some purposes. Newtech-pipes providing the Electric Conduit Pipes & Fittings in Pakistan. Newtech-Pipes manufactures a complete range of electrical conduit pipes and fittings. Keeping in view of quality. Call Us Now: +92333-5665265 / +92 51 4438601-4, Visit Our Website: newtech-pipes.com, Owner Name: Talha kazmi, Email: [email protected]
You are absolutely correct and thanks for giving information about project procurement . I loved your blog and thanks for publishing this!! I am really happy to come across this exceptionally well written content. Thanks for sharing and look for more in future!! You must also check out Dukeswiremesh.com it has some great insights too.
Good information, CE certification permits organization to lawfully advertise and disseminate their item with Market and Mandates, Guidelines. CE certification in Philippines.